Ultrasonography for confirmation of gastric tube placement
- PMID: 39051488
- PMCID: PMC11270641
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012083.pub3
Ultrasonography for confirmation of gastric tube placement
Abstract
Background: Gastric tubes are commonly used for the administration of drugs and tube feeding for people who are unable to swallow. Feeding via a tube misplaced in the trachea can result in severe pneumonia. Therefore, the confirmation of tube placement in the stomach after tube insertion is important. Recent studies have reported that ultrasonography provides good diagnostic accuracy estimates in the confirmation of appropriate tube placement. Hence, ultrasound could provide a promising alternative to X-rays in the confirmation of tube placement, especially in settings where X-ray facilities are unavailable or difficult to access.
Objectives: To assess the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound alone or in combination with other methods for gastric tube placement confirmation in children and adults.
Search methods: This systematic review is an update of a previously published Cochrane review. For this update, we searched the Cochrane Library (2021, Issue 6), MEDLINE (to April 2023), Embase (to April 2023), five other databases (to July 2021), and reference lists of articles, and contacted study authors.
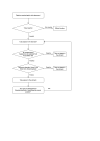
Selection criteria: We included studies that evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of naso- and orogastric tube placement confirmed by ultrasound visualization using X-ray visualization as the reference standard. We included cross-sectional studies and case-control studies. We excluded case series or case reports. We excluded studies if X-ray visualization was not the reference standard or if the tube being placed was a gastrostomy or enteric tube.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed the methodological quality and extracted data from each of the included studies. We contacted the authors of the included studies to obtain missing data. There were sparse data for specificity. Therefore, we performed a meta-analysis of only sensitivity using a univariate random-effects logistic regression model to combine data from studies that used the same method and echo window.
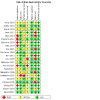
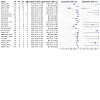
Main results: We identified 12 new studies in addition to 10 studies included in the earlier version of this review, totalling 1939 participants and 1944 tube insertions. Overall, we judged the risk of bias in the included studies as low or unclear. No study was at low risk of bias or low concern for applicability in every QUADAS-2 domain. There were limited data (152 participants) for misplacement detection (specificity) due to the low incidence of misplacement. The summary sensitivity of ultrasound on neck and abdomen echo windows were 0.96 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.92 to 0.98; moderate-certainty evidence) for air injection and 0.98 (95% CI 0.83 to 1.00; moderate-certainty evidence) for saline injection. The summary sensitivity of ultrasound on abdomen echo window was 0.96 (95% CI 0.65 to 1.00; very low-certainty evidence) for air injection and 0.97 (95% CI 0.95 to 0.99; moderate-certainty evidence) for procedures without injection. The certainty of evidence for specificity across all methods was very low due to the very small sample size. For settings where X-ray was not readily available and participants underwent gastric tube insertion for drainage (8 studies, 552 participants), sensitivity estimates of ultrasound in combination with other confirmatory tests ranged from 0.86 to 0.98 and specificity estimates of 1.00 with wide CIs. For studies of ultrasound alone (9 studies, 782 participants), sensitivity estimates ranged from 0.77 to 0.98 and specificity estimates were 1.00 with wide CIs or not estimable due to no occurrence of misplacement.
Authors' conclusions: Of 22 studies that assessed the diagnostic accuracy of gastric tube placement, few studies had a low risk of bias. Based on limited evidence, ultrasound does not have sufficient accuracy as a single test to confirm gastric tube placement. However, in settings where X-ray is not readily available, ultrasound may be useful to detect misplaced gastric tubes. Larger studies are needed to determine the possibility of adverse events when ultrasound is used to confirm tube placement.
Copyright © 2024 The Cochrane Collaboration. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
YT: is a board member of Cochrane Japan, and received grants from JSPS Kakenhi Grant Number 22K10423, Pfizer Health Research Foundation, and Kyoto University School of Public Health for work other than this review. YT is a Cochrane Editor but was not involved in the editorial process.
YK: received grants from JSPS Kakenhi Grant Number 22K15664, SRWS‐PSG, and Yasuda Memorial Medical Foundation Grant Program for Cancer Research for work other than this review.
MB: none.
KA: received grants from SRWS‐PSG, Fujiwara Memorial Foundation, Research Institute of Healthcare Data Science for work other than this review, and JSPS Kakenhi Grant Number 24K19108.
AS: none.
SJ: none.
Figures


Update of
-
Ultrasonography for confirmation of gastric tube placement.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 17;4(4):CD012083. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012083.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Jul 25;7:CD012083. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012083.pub3. PMID: 28414415 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abily 2019 {published data only}
-
- Abily J, Derville S, Lemaitre C, Lagache L, Grange S, Carpentier D, et al. Confirming gastric tube placement in ICU: effectiveness of gastric ultrasonography. Annals of Intensive Care 2018;8(Suppl 1):F-50.
-
- Abily J, Derville S, Scherrer V, Compere V, Lemaitre C, Carpentier D, et al. Performance of gastric ultrasonography to validate the positioning of gastric tube in intensive care. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental 2019;7:-.
Atalay 2016 {published data only}
-
- Atalay YO, Aydin R, Ertugrul O, Gul SB, Polat AV, Paksu MS. Does bedside sonography effectively identify nasogastric tube placements in pediatric critical care patients? Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2016;31(6):805-9. - PubMed
Basile 2015 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Basile V, Cresci A, Brondi B, Solinas D, Cei M, Mumoli N. Nurse ultrasound evaluation as an alternative to whoosh test for nasogastric tube placement verification. Italian Journal of Medicine 2015;9(s2):5.
Brun 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Brun PM, Chenaitia H, Bessereau J, Leyral J, Barberis C, Pradel-Thierry AL, et al. Ultrasound evaluation of the nasogastric tube position in prehospital [Contrôle échographique de la position de la sonde nasogastrique en préhospitalier]. Annales Francaises d'Anesthesie et de Reanimation 2012;31(5):416-20. [DOI: 10.1016/j.annfar.2012.01.029] - DOI - PubMed
Brun 2014 {published data only}
Chenaitia 2012 {published data only}
Claiborne 2020 {published data only}
-
- Claiborne M, Gross T, McGreevy J, Riemann M, Temkit M, Augenstein J. Point-of-care ultrasound for confirmation of nasogastric and orogastric tube placement in pediatric patients. Pediatric Emergency Care 2020;37(12):e1611-5. - PubMed
Dias 2019 {published data only}
-
- Dias FS, Alvares BR, Jales RM, Franco AP, Silva JE, Fabene SM, et al. The use of ultrasonography for verifying gastric tube placement in newborns. Advances in Neonatal Care 2019;19(3):219-25. - PubMed
Gok 2015 {published and unpublished data}
Güllüpınar 2022 {published data only}
-
- Güllüpınar B, Sağlam C, Karagöz A, Tandon S. Nasogastric tube placement verification with ultrasound by emergency nurses nasogastric tube placement verification with ultrasound applied by nurses. Annals of Clinical and Analytical Medicine 2022;13(7):807-11.
Kim 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kim HM, So BH, Jeong WJ, Choi SM, Park KN. The effectiveness of ultrasonography in verifying the placement of a nasogastric tube in patients with low consciousness at an emergency center. Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine 2012;20(1):38. [DOI: 10.1186/1757-7241-20-38] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lock 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lock G, Reng CM, Koellinger M, Rogler G, Schoelmerich J, Schlottmann K. Sonographic control of gastric tube placement on the intensive care unit [Sonographische Kontrolle von Magensonden bei Intensivpatienten]. Intensivmedizin und Notfallmedizin 2003;40(8):693-7. [DOI: 10.1007/s00390-003-0417-9] - DOI
McMullen 2021 {published data only}
-
- McMullen C, Garrett P, Moore J, Anstey C. Nasogastric tube placement under sonographic observation: a comparison study of ultrasound and chest radiography in mechanically ventilated patients. Australian Critical Care 2021;35(2):181-5. - PubMed
Mumoli 2021 {published data only}
-
- Mumoli N, Barberio M, Mereghetti M, Rotiroti G, Cei M, Cresci A, et al. Abdominal ultrasound in nasogastric tube placement: a multicenter, prospective, cohort study. Italian Journal of Medicine 2019;13:40.
-
- Mumoli N, Vitale J, Pagnamenta A, Mastroiacovo D, Cei M, Pomero F, et al. Bedside abdominal ultrasound in evaluating nasogastric tube placement: a multicenter, prospective, cohort study. Chest 2021;159(6):2366-72. - PubMed
Nedel 2017 {published data only}
Nikandros 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Nikandros M, Skampas N, Theodorakopoulou M, Ioannidou S, Theotokas M, Armaganidis A. Sonography as a tool to confirm the position of the nasogastric tube in ICU patients. Critical Care 2006;10(Suppl 1):P216. [DOI: 10.1186/cc4563] - DOI
Radulescu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Radulescu V, Ahmad S. Ultrasound confirmation of gastric tube placement: a novel method. Chest 2015;148(4):508A-B. [DOI: 10.1378/chest.2264258] - DOI
Tai 2016 {published data only}
-
- Tai PH, Lau WS, Chan PY, Ng SY, Lam YC, Mak HT, et al. Nurse performed ultrasonography in confirming the position of nasogastric tube in the emergency department: a prospective single group diagnostic test study. Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine 2016;23(6):340-9.
Vigneau 2005 {published data only}
Wong 2017 {published data only}
-
- Wong KW, Chan HH, Wong CP, Chan MY, Chau JC, Wong TW. Using color flow detection of air insufflation to improve accuracy in verifying nasogastric tube position. American Journal of Emergency Medicine 2017;35(2):333-6. - PubMed
Yildirim 2018 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Acosta Pedemonte 2020 {published data only}
-
- Acosta Pedemonte NB, Bagilet DH, Rocchetti NS, Torresan GV, Rodriguez NA, Settecase CJ. Color doppler ultrasound is a precise method to evaluate the position of the nasogastric tube in critical ill patients. Medicina Intensiva 2020;45(7):e11-4. - PubMed
Atalay 2019 {published data only}
Barberio 2018 {published data only}
-
- Barberio M, Rimoldi A, Grittini A, Venegoni E, Mazzotti J, Mumoli N. Ultrasound evaluation as an alternative to whoosh test for nasogastric tube placement verification. Italian Journal of Medicine 2018;12(2):25.
Blaivas 2012 {published data only}
-
- Blaivas M. Ultrasound confirmation of nasogastric tube placement in the pre-hospital setting: so why is this of any interest? Resuscitation 2012;83(4):409-10.
Brotfain 2019 {published data only}
-
- Brotfain E, Erblat A, Luft P, Elir A, Koyfman L, Israeli L, et al. Ultrasound (US) assessment of gastric content, volume and nasal/ oral gastric tube placement in general intensive care unit (GICU) (preliminary results). Critical Care 2019;23:-. - PubMed
Carmona 2018 {published data only}
-
- Carmona EV. Comparison of three methods to measure the feeding tube in newborns. Registro Brasileiro de Ensaios Clínicos (ReBEC), RBR-2zk6yc; 2018. [REGISTRO BRASILEIRO DE ENSAIOS CLÍNICOS (REBEC): https://ensaiosclinicos.gov.br/rg/RBR-2zk6yc]
Choi 2021 {published data only}
-
- Choi E, Korostensky M, Walker A, Spencer A. Validation of sonographic assistance for placement of a nasogastric tube in pediatric patients. Journal of Clinical Ultrasound 2021;49(2):101-5. - PubMed
CTRI//09/027678 {published data only}
-
- CTRI//09/027678. Comparing the use of ultrasound to detect correct gastric tube placement with the currently used method of pushing air into the stomach via gastric tube with a syringe and hearing the sound with the help of stethoscope in ICU patients. https://trialsearch.who.int/Trial2.aspx?TrialID=CTRI/2020/09/027678 (registered 9 September 2020).
Dagli 2015 {published data only}
-
- Dagli R, Bayir H, Dadali Y, Tokmak T, Erbesler Z. Role of ultrasonography in detection of the localization of the nasoenteric tube. Critical Care 2015;19(Suppl 1):S138.
De Robertis 2019 {published data only}
-
- De Robertis E, Romano GM. Are you sure of the "other tube"? Role of ultrasound in the evaluation of gastric tube positioning in the operating room. Minerva Anestesiologica 2019;85(11):1149-50. - PubMed
Edroso 2020 {published data only}
-
- Edroso JP, Monge SL, Vicho PR. Malposition of nasogastric tube diagnosed by ultrasound in abdominal surgery patient. Medicina Intensiva 2020;44(5):321-2. - PubMed
Ferraboli 2022 {published data only}
-
- Ferraboli SF, Beghetto MG. Bedside ultrasonography for the confirmation of nasogastric tube placement: agreement between nurse and physician. Revista Gaucha de Enfermagem 2022;43:e20220211. - PubMed
Greenberg 1993 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg M, Bejar R, Asser S. Confirmation of transpyloric feeding tube placement by ultrasonography. Journal of Pediatrics 1993;122(3):413-5. - PubMed
Hernandez‐Socorro 1996 {published data only}
-
- Hernandez-Socorro CR, Marin J, Ruiz-Santana S, Santana L, Manzano JL. Bedside sonographic-guided versus blind nasoenteric feeding tube placement in critically ill patients. Critical Care Medicine 1996;24(10):1690-4. - PubMed
JPRN‐UMIN000027806 {published data only}
-
- JPRN-UMIN000027806. The confirmation of a tracheal tube placement by using ultrasonography (combined with a gastric tube). https://rctportal.niph.go.jp/en/detail?trial_id=UMIN000027806 (first registered 1 July 2017).
Kerforne 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kerforne T, Chaillan M, Geraud L, Mimoz O. Ultrasound diagnosis of nasogastric tube misplacement into the trachea during bypass surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2013;111(6):1032-3. - PubMed
Liu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Liu XF, Zhu HQ, Xu QL, Xie YM. Comparison of two nasal-jejunal tube placement methods in critically ill patients with different acute gastrointestinal injury grades. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University 2015;36:961. [DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1008.2015.00961] - DOI
Lock 1997 {published data only}
-
- Lock G, Reng M, Messman H, Grune S, Scholmerich J, Holstege A. Inflation and positioning of the gastric balloon of a Sengstaken-Blakemore tube under ultrasonographic control. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 1997;45:538. - PubMed
Nasreen 2017 {published data only}
-
- Nasreen M, Amin M, Humayun A, Ali W, Rana HA, Farooq M. Diagnostic accuracy of tracheal rapid ultrasound exam (TRUE) for confirming endotracheal tube placement in emergency intubation using X-ray as gold standard. Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences 2017;11(2):602-4.
NCT03430908 {published data only}
-
- NCT03430908. Blind gastric tube placement: incidence of malposition confirmed by ultrasonography. clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03430908 (first received 7 February 2018).
Pellet 2018 {published data only}
-
- Pellet A, Jafari D, Shofer FS, Wong A, Chan W, Panebianco N. Ultrasound assessment of nasoenteric feeding tube placement. Academic Emergency Medicine 2018;25:S210.
Piton 2017 {published data only}
-
- Piton G, Parel R, Delabrousse E, Capellier G. Echography for nasogastric tube placement verification. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2017;71(5):669-70. - PubMed
Qian 2020 {published data only}
Scarpellini 2019 {published data only}
-
- Scarpellini E, Rasetti C, Santori P, Basilico M, Giostra N, Valeri M, et al. Usefulness of abdominal ultrasound vs. chest X-ray in nasogastric tube positioning check in malnourished patients. Clinical Nutrition 2019;38:S159.
Tamhne 2006 {published data only}
Tsolaki 2022 {published data only}
Wagai 1981 {published data only}
-
- Wagai Y, Kurosaki K. Ultrasonography of the gastrointestinal tube [Hukubukanku-zouki no Choonpa-shindan no Igi]. Rinsho Hoshasen. Clinical Radiography 1981;26(6):649-54. - PubMed
Xiao 2020 {published data only}
Yadav 2020 {published data only}
Yaseen 2022 {published data only}
-
- Yaseen M, Kumar A, Bhoi S, Sinha TP, Jamshed N, Aggarwal P, et al. Point-of-care ultrasonography-assisted nasogastric tube placement in the emergency department: a randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Emergency Medicine 2022;29(6):431-6. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
CTRI//05/019427 {published data only}
-
- CTRI//05/019427. Locating the nasogastric tube using ultrasound technology [Randomized control trial to compare ultrasound guided naso/orogastric tube placement as compared to standard naso/orogastric tube placement in neonates]. https://ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?EncHid=MzQxOTU=&Enc... (registered 29 May 2019). [CLINICAL TRIALS REGISTRIES INDIA (CTRI): https://ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?EncHid=MzQxOTU=&Enc=&us...]
NCT02866123 {published data only}
-
- Verification of correct positioning of a gastric tube by ultrasonography (SNG echo). clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02866123 (first received 4 August 2016).
NCT04104295 {published data only}
-
- The use of ultrasound to determine correct nasogastric tube placement in children admitted to the pediatric ICU: a pilot study. clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04104295 (first received 24 September 2019).
NCT04795895 {published data only}
-
- Ultrasound for confirmation of gastric tube placement in critically ill patients under invasive mechanical ventilation, a randomization trial. clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04795895 (first received 10 March 2021).
Rigobello 2020 {published data only}
Additional references
AACCN 2009
-
- American Association of Critical Care Nurses. AACN practice alert: verification of feeding tube placement (blindly inserted), 2009. www.aacn.org/wd/practice/docs/practicealerts/verification-feeding-tube-p... (accessed 5 February 2016).
Berrington 2004
-
- Berrington de Gonzalez A, Darby S. Risk of cancer from diagnostic X-rays: estimates for the UK and 14 other countries. Lancet 2004;363(9406):345-51. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Beynon 2013
Bloom 2022
-
- Bloom L, Seckel MA. Placement of nasogastric feeding tube and postinsertion care review. AACN Advanced Critical Care 2022;33(1):68-84. - PubMed
Bossuyt 2008
-
- Bossuyt PM, Leeflang MM. Chapter 6: Developing criteria for including studies. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 0.4 (updated September 2008). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from srdta.cochrane.org.
Bossuyt 2015
Boullata 2017
-
- Boullata JI, Carrera AL, Harvey L, Escuro AA, Hudson L, Mays A, et al. ASPEN safe practices for enteral nutrition therapy. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2017;41(1):15-103. - PubMed
Bourgault 2009
-
- Bourgault AM, Halm MA. Feeding tube placement in adults: safe verification method for blindly inserted tubes. American Journal of Critical Care 2009;18(1):73-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
CNSC 2013
-
- Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission. Linear-non-threshold model. Fact sheet April 2013. nuclearsafety.gc.ca/eng/pdfs/reading-room/healthstudies/Fact-Sheet-Linea... (accessed 13 April 2017).
de Vet 2008
-
- Vet HC, Eisinga A, Riphagen II, Aertgeerts B, Pewsner D. Chapter 7: Searching for studies. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 0.4 (updated September 2008). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from srdta.cochrane.org.
Deeks 2013
-
- Deeks JJ, Wisniewski S, Davenport C. Chapter 4: Guide to the contents of a Cochrane diagnostic test accuracy protocol. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2013. Available from https://srdta.cochrane.org.
Deeks 2023
-
- Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Leeflang MM, Takwoingi Y, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy. Version 2.0 (updated July 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from https://training.cochrane.org/handbook-diagnostic-test-accuracy/current. - PMC - PubMed
Der Kureghian 2011
-
- Der Kureghian J, Kumar S, Jani P. Nasogastric tube insertion in difficult cases with the aid of a flexible nasendoscope. Journal of Laryngology and Otology 2011;125(9):962-4. - PubMed
ECRI and ISMP 2006
-
- ECRI Institute and Institute for Safe Medication Practices. Confirming feeding tube placement: old habits die hard. Pennsylvania Patient Safety Authority 2006;3(4):1-10. [patientsafetyauthority.org/ADVISORIES/AdvisoryLibrary/2006/Dec3(4)/docum...
ENA 2015
-
- ENA Clinical Practice Guideline Committee. Clinical practice guideline: gastric tube placement verification, 2015. www.ena.org/practice-research/research/CPG/Documents/GastricTubeCPG.pdf (accessed 4 October 2016).
ENA 2019
-
- ENA Clinical Practice Guideline Committee, Killian M, Reeve NE, Slivinski A, Bradford JY, Horigan A, Barnason S, et al. Clinical practice guideline: gastric tube placement verification. Journal of Emergency Nursing 2019;45(3):306.e1-e19. - PubMed
ESPN guidelines 2020
-
- Pironi L, Boeykens K, Bozzetti F, Joly F, Klek S, Lal S, et al. ESPEN guideline on home parenteral nutrition. Clinical Nutrition 2020;39:1645-66. - PubMed
Frush 2003
-
- Frush DP, Donnelly LF, Rosen NS. Computed tomography and radiation risks: what pediatric health care providers should know. Pediatrics 2003;112(4):951-7. - PubMed
Glas 2003
-
- Glas AS, Lijmer JG, Prins MH, Bonsel GJ, Bossuyt PM. The diagnostic odds ratio: a single indicator of test performance. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2003;56(11):1129-35. [PMID: ] - PubMed
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- GRADEpro GDT. McMaster University and Evidence Prime, Version accessed 3 October 2023. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2023. Available at https://www.gradepro.org.
Harbord 2009
-
- Harbord RM, Whiting P. metandi: meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy using hierarchical logistic regression. Stata Journal 2009;9(2):211-29.
Holland 2013
-
- Holland A, Smith F, Penny K. Carbon dioxide detection for testing nasogastric tube placement in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 10. Art. No: CD010773. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010773] - DOI
IHS Markit 2018
-
- IHS Markit. The global ultrasound equipment market in 2018. https://cdn.ihs.com/www/pdf/IHS%20Markit%20-%20The%20Global%20Ultrasound... (accessed 12 July 2024).
Irving 2014
-
- Irving SY, Lyman B, Northington L, Bartlett JA, Kemper C. Nasogastric tube placement and verification in children: review of the current literature. Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2014;29(3):267-76. - PubMed
JSPEN Guideline 2013
-
- Japanese Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. JSPEN guideline for parenteral and enteral nutrition. Jomyaku Keicho Eiyo 2013;28:1195-9. [DOI: 10.11244/jjspen.28.1195] - DOI
Kawati 2005
-
- Kawati R, Rubertsson S. Malpositioning of fine bore feeding tube: a serious complication. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2005;49(1):58-61. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lamont 2011
-
- Lamont T, Beaumont C, Fayaz A, Healey F, Huehns T, Law R, et al. Checking placement of nasogastric feeding tubes in adults (interpretation of x ray images): summary of a safety report from the National Patient Safety Agency. BMJ 2011;342:2586. - PubMed
Lin 2017
-
- Lin T, Gifford W, Lan Y, Qin X, Liu X, Wang J, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography for detecting nasogastric tube (NGT) placement in adults: a systematic review and meta analysis. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2017;71:80-8. - PubMed
Mariani 2010
-
- Mariani PJ, Setla JA. Palliative ultrasound for home care hospice patients. Academic Emergency Medicine 2010;17:293-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Metheny 1999
-
- Metheny NA, Stewart BJ, Smith L, Yan H, Diebold M, Clouse RE. pH and concentration of bilirubin in feeding tube aspirates as predictors of tube placement. Nursing Research 1999;48(4):189-97. - PubMed
Metheny 2019
-
- Metheny NA, Krieger MM, Healey F, Meert KL. A review of guidelines to distinguish between gastric and pulmonary placement of nasogastric tubes. Heart Lung 2019;48(3):226-35. - PubMed
Milsom 2015
-
- Milsom SA, Sweeting JA, Sheahan H, Haemmerle E, Windsor JA. Naso-enteric tube placement: a review of methods to confirm tip location, global applicability and requirements. World Journal of Surgery 2015;39:2243-52. - PubMed
National Patient Safety Agency 2011
-
- National Patient Safety Agency. Patient Safety Alert NPSA/2011/PSA002: reducing the harm caused by misplaced nasogastric feeding tubes in adults, children and infants, March 2011. www.nrls.npsa.nhs.uk/EasySiteWeb/getresource.axd?AssetID=129697 (accessed 13 April 2017).
NHS Improvement 2016
-
- NHS Improvement. Nasogastric tube misplacement: continuing risk of death and severe harm. https://www.england.nhs.uk/2016/07/nasogastric-tube-misplacement-continu... (accessed prior to 30 June 2024).
NICE 2006
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Nutrition support for adults: oral nutrition support, enteral tube feeding and parenteral nutrition (CG32), 2006. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg32 (accessed 13 April 2017). - PubMed
RevMan 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.0.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020. Available at https://revman.cochrane.org.
Samuels 2013
-
- Samuels LE. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine. 6th edition. Philadelphia (PA): Saunders, 2013.
SCCM and ASPEN Guidelines 2016
-
- McClave SA, Taylor BE, Martindale RG, Warren MM, Johnson DR, Braunschweig C, et al. Guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.). Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2016;40:159-211. - PubMed
Schünemann 2020
-
- Schünemann HJ, Mustafa RA, Brozek J, Steingart KR, Leeflang M, Murad MH, et al. GRADE guidelines: 21 part 2. Test accuracy: inconsistency, imprecision, publication bias, and other domains for rating the certainty of evidence and presenting it in evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2020;122:142-52. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.12.021] - DOI - PubMed
Simons 2012
-
- Simons SR, Abdallah LM. Bedside assessment of enteral tube placement: aligning practice with evidence. American Journal of Nursing 2012;112:40-6. - PubMed
Sparks 2011
Takwoingi 2013
-
- Takwoingi Y. Meta-analysis of test accuracy studies in Stata: a bivariate model approach. Test Accuracy Meta-analysis in Stata 2013:1-30.
Taylor 2021
Thomson 2000
-
- Thomson F, Naysmith M, Lindsay A. Managing drug therapy in patients receiving enteral and parenteral nutrition. Hospital Pharmacist 2000;7(6):155-64.
Torsy 2020
-
- Torsy T, Saman R, Boeykens K, Duysburgh I, Eriksson M, Verhaeghe S, et al. Accuracy of the corrected nose-earlobe-xiphoid distance formula for determining nasogastric feeding tube insertion length in intensive care unit patients: a prospective observational study. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2020;110:103614. - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529-36. [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Tsujimoto 2016
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

