PharmVar GeneFocus: CYP2A6
- PMID: 39051767
- PMCID: PMC11452280
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.3387
PharmVar GeneFocus: CYP2A6
Abstract
The Pharmacogene Variation Consortium (PharmVar) provides nomenclature for the human CYP2A gene locus containing the highly polymorphic CYP2A6 gene. CYP2A6 plays a role in the metabolism of nicotine and various drugs. Thus, genetic variation can substantially contribute to the function of this enzyme and associated efficacy and safety. This GeneFocus provides an overview of the clinical significance of CYP2A6, including its genetic variation and function. We also highlight and discuss caveats in the identification and characterization of allelic variation of this complex pharmacogene, a prerequisite for accurate genotype determination and prediction of phenotype status.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interests
C.N. and G.S are employed by PharmGenetix GmbH, a private laboratory providing PGx testing, reporting, and interpretation services. All other authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures
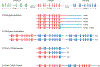



References
-
- Nagata K, Matsunaga T, Gillette J, Gelboin HV, Gonzalez FJ. Rat testosterone 7 alpha-hydroxylase. Isolation, sequence, and expression of cDNA and its developmental regulation and induction by 3-methylcholanthrene. J Biol Chem. Feb 25 1987;262(6):2787–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

