Maternal regulation of the vertebrate oocyte-to-embryo transition
- PMID: 39052672
- PMCID: PMC11302925
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011343
Maternal regulation of the vertebrate oocyte-to-embryo transition
Abstract
Maternally-loaded factors in the egg accumulate during oogenesis and are essential for the acquisition of oocyte and egg developmental competence to ensure the production of viable embryos. However, their molecular nature and functional importance remain poorly understood. Here, we present a collection of 9 recessive maternal-effect mutants identified in a zebrafish forward genetic screen that reveal unique molecular insights into the mechanisms controlling the vertebrate oocyte-to-embryo transition. Four genes, over easy, p33bjta, poached and black caviar, were found to control initial steps in yolk globule sizing and protein cleavage during oocyte maturation that act independently of nuclear maturation. The krang, kazukuram, p28tabj, and spotty genes play distinct roles in egg activation, including cortical granule biology, cytoplasmic segregation, the regulation of microtubule organizing center assembly and microtubule nucleation, and establishing the basic body plan. Furthermore, we cloned two of the mutant genes, identifying the over easy gene as a subunit of the Adaptor Protein complex 5, Ap5m1, which implicates it in regulating intracellular trafficking and yolk vesicle formation. The novel maternal protein Krang/Kiaa0513, highly conserved in metazoans, was discovered and linked to the function of cortical granules during egg activation. These mutant genes represent novel genetic entry points to decipher the molecular mechanisms functioning in the oocyte-to-embryo transition, fertility, and human disease. Additionally, our genetic adult screen not only contributes to the existing knowledge in the field but also sets the basis for future investigations. Thus, the identified maternal genes represent key players in the coordination and execution of events prior to fertilization.
Copyright: © 2024 Fuentes et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: A.J.G. is founder of and has an equity interest in RESA Therapeutics, Inc. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
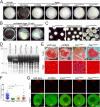
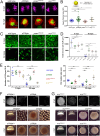
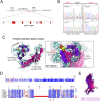

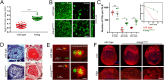
References
-
- Lindeman RE, Pelegri F. Vertebrate maternal-effect genes: Insights into fertilization, early cleavage divisions, and germ cell determinant localization from studies in the zebrafish. Mol Reprod Dev. 2010;77(4):299–313. Epub 2009/11/13. doi: 10.1002/mrd.21128 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC4276564. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 GM077835/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD007516/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD100035/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM103789/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM131908/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM122580/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD074078/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM080926/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD094096/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG012969/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD069321/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

