Deficient Generation of Spike-Specific Long-Lived Plasma Cells in the Bone Marrow After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection
- PMID: 39052732
- PMCID: PMC11272043
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiad603
Deficient Generation of Spike-Specific Long-Lived Plasma Cells in the Bone Marrow After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection
Abstract
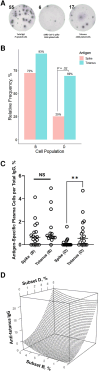
Generation of a stable long-lived plasma cell (LLPC) population is the sine qua non of durable antibody responses after vaccination or infection. We studied 20 individuals with a prior coronavirus disease 2019 infection and characterized the antibody response using bone marrow aspiration and plasma samples. We noted deficient generation of spike-specific LLPCs in the bone marrow after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection. Furthermore, while the regression model explained 98% of the observed variance in anti-tetanus immunoglobulin G levels based on LLPC enzyme-linked immunospot assay, we were unable to fit the same model with anti-spike antibodies, again pointing to the lack of LLPC contribution to circulating anti-spike antibodies.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; humoral immunity; immunological memory; plasma cells.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of early COVID-19 treatment with convalescent plasma on antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Jul;13(7):e0300624. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03006-24. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 40488473 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 total immunoglobulin and neutralising antibody responses in healthy blood donors throughout the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal observational study.Swiss Med Wkly. 2024 Jul 1;154:3408. doi: 10.57187/s.3408. Swiss Med Wkly. 2024. PMID: 39137369
-
Limited Variation between SARS-CoV-2-Infected Individuals in Domain Specificity and Relative Potency of the Antibody Response against the Spike Glycoprotein.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0267621. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02676-21. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35080430 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibodies to prevent COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 17;6(6):CD014945. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014945.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35713300 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Immune Imprinting, Non-Durable Hybrid Immunity, and Hybrid Immune Damping Following SARS-CoV-2 Primary Vaccination with BNT162b2 and Boosting with mRNA-1273.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Mar 13;13(3):310. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13030310. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40266217 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-specific plasma cells are not durably established in the bone marrow long-lived compartment after mRNA vaccination.Nat Med. 2025 Jan;31(1):235-244. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03278-y. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 39333316 Free PMC article.
-
Longevity of antibody responses is associated with distinct antigen-specific B cell subsets early after infection.Front Immunol. 2024 Dec 17;15:1505719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1505719. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39742271 Free PMC article.
-
The Majority of SARS-CoV-2 Plasma Cells are Excluded from the Bone Marrow Long-Lived Compartment 33 Months after mRNA Vaccination.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 13:rs.3.rs-3979237. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3979237/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Med. 2025 Jan;31(1):235-244. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03278-y. PMID: 38559048 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Insect-specific virus platforms for arbovirus vaccine development.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 14;16:1521104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1521104. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40160816 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01 BX005469/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- 2R56AI110259-06/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1UL1TR003098/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences Clinical Translational Science Award
- P01 AI162242/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- BX005469-01/US Department of Veterans Affairs Biomedical Laboratory Research and Development Service
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

