Pericyte response to ischemic stroke precedes endothelial cell death and blood-brain barrier breakdown
- PMID: 39053491
- PMCID: PMC11571979
- DOI: 10.1177/0271678X241261946
Pericyte response to ischemic stroke precedes endothelial cell death and blood-brain barrier breakdown
Abstract
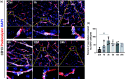
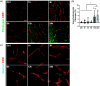
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death and disability, yet the cellular response to the ischemic insult is poorly understood limiting therapeutic options. Brain pericytes are crucial for maintaining blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity and are known to be one of the first responders to ischemic stroke. The exact timeline of cellular events after stroke, however, remains elusive. Using the permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion stroke model, we established a detailed timeline of microvascular events after experimental stroke. Our results show that pericytes respond already within 1 hour after the ischemic insult. We find that approximately 30% of the pericyte population dies as early as 1 hour after stroke, while ca 50% express markers that indicate activation. A decrease of endothelial tight junctions, signs of endothelial cell death and reduction in blood vessel length are only detected at time points after the initial pericyte response. Consistently, markers of BBB leakage are observed several hours after pericyte cell death and/or vascular detachment. Our results suggest that the pericyte response to stroke occurs early and precedes both the endothelial response and the BBB breakdown. This highlights pericytes as an important target cell type to develop new diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; endothelial cells; ischemia; pericytes; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures




References
-
- Timmis A, Townsend N, Gale C, ESC Scientific Document Group et al. European society of cardiology: Cardiovascular disease statistics 2017. Eur Heart J 2018; 39: 508–579. - PubMed
-
- Campbell BCV, Mitchell PJ, Investigators E-I, Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2015; 372: 2365–2366. - PubMed
-
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, ECASS Investigators et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2008; 359: 1317–1329. - PubMed
-
- Larrue V, von Kummer R, del Zoppo G, et al. Hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke. Potential contributing factors in the european cooperative acute stroke study. Stroke 1997; 28: 957–960. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

