Effectiveness of secukinumab in radiographic and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a European routine-care observational study
- PMID: 39053949
- PMCID: PMC11284936
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2024-004166
Effectiveness of secukinumab in radiographic and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a European routine-care observational study
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the treatment effectiveness of secukinumab in radiographic (r) versus non-radiographic (nr) axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) patients treated in routine care across Europe.
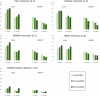
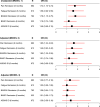
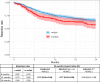
Methods: Prospectively collected data on secukinumab-treated axSpA patients with known radiographic status were pooled from nine countries.Remission rates based on patient-reported outcomes (PROs; Numeric Rating Scale (0-10), for example, pain ≤2/Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≤2 and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) inactive disease (ID) <1.3 after 6/12/24 months of secukinumab treatment were calculated.Remission and drug retention rates in r-axSpA versus nr-axSpA patients were compared by logistic and Cox regression models (unadjusted/adjusted for age+sex/adjusted for multiple confounders).
Results: Overall, 1161 secukinumab-treated patients were included (r-axSpA/nr-axSpA: 922/239). At baseline, r-axSpA patients had longer disease duration and higher C reactive protein, were more often male and HLA-B27 positive and had received fewer prior biological or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs compared with nr-axSpA patients, whereas PROs were largely similar.During follow-up, crude PRO remission rates were significantly higher in r-axSpA compared with nr-axSpA patients (6 months: pain≤2: 40%/28%, OR=1.7; BASDAI≤2: 37%/25%, OR=1.8), as were drug retention rates (24 months: 66%/58%, HR 0.73 (ref: r-axSpA)). Proportions of patients achieving ASDAS ID were low for both groups, particularly nr-axSpA (6 months: 11%/8%).However, when adjusting for age+sex, these differences diminished, and after adjusting for multiple confounders, no significant between-group differences remained for either remission or drug retention rates.
Conclusion: Crude remission/drug retention rates in European secukinumab-treated patients were higher in r-axSpA compared with nr-axSpA patients. In adjusted analyses, secukinumab effectiveness was similar in both groups, suggesting that observed differences were related to factors other than radiographic status.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Pain; Patient Reported Outcome Measures; Spondylitis, Ankylosing; Therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SNC: Speaker fees BMS and GE, Research grant from Novartis (paid to the employer). SHR: Research grant from Novartis (paid to the employer). MO: Speaker and/or consultancy fees from AbbVie, BMS, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Celgene, Eli-Lilly, Hospira, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Novo, Orion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi, UCB. Research grants from AbbVie, BMS, Merck, Novartis and UCB. MP: Research grant from Novartis (paid to the employer). Speaker fees: Sandoz. Brigitte Michelsen: Consulting fees from Novartis. Research grant from Novartis (paid to employer). KP: Consultancy fees: AbbVie, UCB, Pfizer, Eli Lilly, Celltrion, MSD and Novartis. Catalin Codreanu: Speaker and consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Ewopharma, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer. Adrian Ciurea: None. Bente Glintborg: Research grants from Pfizer, Abbvie, BMS, Sandoz. MJS: Speaker fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Lilly, Medac, Novartis, Pfizer. Ismail Sari: None. ZR: Speaker and consultancy fees from Abbvie, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Janssen, SOBI, Swixx BioPharma, AstraZeneca, Amgen, MSD, Medis, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Lek. BG: Speaker and consultancy fees from Novartis and Nordic-Pharma. GJM: Research grant from GSK. HR: Consulting and/or speaking fees from AbbVie, Celgene, Pfizer, UCB, Viatris. FI: None. Karin Laas: Speakers fees from AbbVie, Johnson and Johnson, Novartis, Pfizer. JKW: Speaker fees from AbbVie, Amgen. Research support from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer. MvdS: Consultant for Novartis, AbbVie, Eli Lilly UCB, Speakers fee: Novartis, UCB, Janssen, Grant/research support: UCB, Janssen, Novartis, Eli Lilly. Sella Aarrestad Provan: Consultancy fees and Research grants from Boehringer Ingelheim. IC: Speaker and/or consultancy fees from BMS, Eli-Lilly, Galapagos, Gilead, Janssen, Novartis, MSD, Pfizer, GSK. JZ: Speakers fees from AbbVie, Elli-Lilly, Sandoz, Novartis, Egis, UCB, Sanofi, Astra Zeneca, Sobi. CM: None. MJN: Speaker and/or consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Janssens, Novartis, Pfizer. Research grants from Novartis and Pfizer. AGL: Speaking and/or consulting fees from AbbVie, Janssen, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB. Research grant from Novartis. AB: Speaker and/or consultancy fees from AbbVie, Lilly, Janssen and Novartis. YE: None. Katja Perdan Pirkmajer: Speaker and/or consultancy fees from AbbVie, Novartis, MSD, Medis, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Lek, Janssen and Boehringer Ingelheim. GG: None. GTJ: Speaker fee from Janssen. Research grants (paid to employer) from AbbVie, Pfizer, UCB, Amgen, GSK. A-MH: Grant/research support from MSD. MSC: None. SV: None. DdG: None. TKK: Speaker and/or consultancy fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Celltrion, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Sandoz, UCB and Grünenthal. LO-V: None. IvdH-B: Speaker and/or consultancy fees from AbbVie, UCB, MSD, Novartis, Lilly. Unrestricted Grants received for investigator initiated studies from MSD, Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB. Fees received for Lectures from BMS, AbbVie, Pfizer, MSD, UCB. MLH: Advisory Board AbbVie (No personal income, paid to institution). Prev. chaired the steering committee of the Danish Rheumatology Quality Registry (DANBIO, DRQ), which receives public funding from the hospital owners and funding from pharmaceutical companies. Speaker for Pfizer, Medac, Sandoz (no personal income, institution). Research grants (institution) from AbbVie, Biogen, BMS, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Janssen Biologics B.V, Lundbeck Fonden, MSD, Medac, Pfizer, Roche, Samsung Biopies, Sandoz, Novartis, Nordforsk. LMO: Research grant from Novartis (paid to the employer).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
