Benzene: A critical review on measurement methodology, certified reference material, exposure limits with its impact on human health and mitigation strategies
- PMID: 39054826
- PMCID: PMC11294662
- DOI: 10.5620/eaht.2024012
Benzene: A critical review on measurement methodology, certified reference material, exposure limits with its impact on human health and mitigation strategies
Abstract
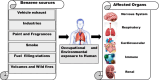
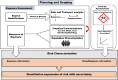
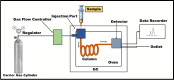
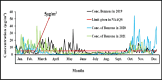
Benzene is a carcinogenic pollutant with significant emission sources present in the atmosphere. The need for accurate and precise measurement of benzene in the atmosphere has become increasingly evident due to its toxicity and the adverse health effects associated with exposure to different concentrations. Certified reference material (CRM) is essential to establish the traceability of measurement results. The present review compiles the available national and international measurement methods, certified reference materials (CRMs) for benzene and the limit of benzene in fuel composition (v/v) worldwide. Overall, the review indicates the benzene level in the atmosphere and the resulting impacts on the environment and human health, which frequently exceed the exposure limits of different environment regulatory agencies. An extensive literature review was conducted to gather information on monitoring and analysis methods for benzene, revealing that the most preferred method, i.e. Gas Chromatography- Flame Ionization Detector and Mass Spectrometry, is neither cost-effective nor suitable for real-time continuous monitoring. By analysing existing literature and studies, this review will shed light on the understanding of the importance of benzene pollution monitoring in ambient air and its implications for public health. Additionally, it will reflect the mitigation strategies applied by regulators & need for future revisions of air quality guidelines.
Keywords: Benzene; Certified reference materials; Exposure limits; Standard measurement methods of benzene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A new certified reference material for benzene measurement in air on a sorbent tube: development and proficiency testing.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Nov;398(5):2265-77. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-4123-8. Epub 2010 Sep 12. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20835870
-
Analysis of benzene air quality standards, monitoring methods and concentrations in indoor and outdoor environment.Heliyon. 2019 Nov 29;5(11):e02918. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02918. eCollection 2019 Nov. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31844766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personal and ambient exposures to air toxics in Camden, New Jersey.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2011 Aug;(160):3-127; discussion 129-51. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2011. PMID: 22097188
-
Characterisation of urban inhalation exposures to benzene, formaldehyde and acetaldehyde in the European Union: comparison of measured and modelled exposure data.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2008 Jul;15(5):417-30. doi: 10.1007/s11356-008-0013-4. Epub 2008 May 20. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2008. PMID: 18491156
-
The Minderoo-Monaco Commission on Plastics and Human Health.Ann Glob Health. 2023 Mar 21;89(1):23. doi: 10.5334/aogh.4056. eCollection 2023. Ann Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 36969097 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- United States, Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Toxicological review of Rev. Lit. Arts Am. [cited Nov 13, 2023]. Available from: http://www.epa.gov/iris/toxreviews/0070tr.pdf.
-
- Kumari P, Garg G, Soni D, Aggarwal SG. Measurement of benzene and other volatile organic compounds: implications for its inhalation health risk associated with the workers at a fuel station in Delhi. Asian Journal of Atmospheric Environment. 2023;17(7):1–11. doi: 10.1007/s44273-023-00007-8. - DOI
-
- Kumari P, Soni D, Aggarwal SG, Singh K. Seasonal and diurnal measurement of ambient benzene at a high traffic inflation site in Delhi: Health risk assessment and its possible role in ozone formation pathways. Environ Anal Health Toxicol. 2023;38(3):e2023016. doi: 10.5620/eaht.2023016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chaudhary S, Kumar A. Study on refuelling pump stations caused by BTEX compounds in firozabad city. International Archive of Applied Sciences and Technology. 2012;3(2):75–79.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

