Impact of Simulation-based Mastery Learning on Management of Massive Hemoptysis
- PMID: 39055331
- PMCID: PMC11270234
- DOI: 10.34197/ats-scholar.2023-0120IN
Impact of Simulation-based Mastery Learning on Management of Massive Hemoptysis
Abstract
Background: The management of massive hemoptysis is a high-risk, low-volume procedure that is associated with high mortality rates, and pulmonary and critical care medicine (PCCM) fellows often lack training. Simulation-based mastery learning (SBML) is an educational strategy that improves skill but has not been applied to massive hemoptysis management.
Objective: This pilot study aimed to develop a high-fidelity simulator, implement an SBML curriculum, and evaluate the impact on PCCM fellows managing massive hemoptysis.
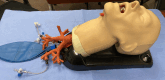
Methods: We modified a simulator to bleed from segmental airways. Next, we developed an SBML curriculum and a validated 26-item checklist and set a minimum passing standard (MPS) to assess massive hemoptysis management. A cohort of traditionally trained providers was assessed using the checklist. First-year PCCM fellows reviewed a lecture before a pretest on the simulator using the skills checklist and underwent rapid-cycle deliberate practice with feedback. Subsequently, fellows were posttested on the simulator, with additional training as necessary until the MPS was met. We compared pretest and posttest performance and also compared SBML-trained fellows versus traditionally trained providers.
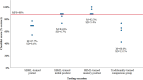
Results: The MPS on the checklist was set at 88%. All first-year PCCM fellows (N = 5) completed SBML training. Mean checklist scores for SBML participants improved from 67.7 ± 8.4% (standard deviation) at pretest to 84.6 ± 6.7% at the initial posttest and 92.3 ± 5.4% at the final (mastery) posttest. Traditionally trained participants had a mean test score of 60.6 ± 13.1%.
Conclusion: The creation and implementation of a massive hemoptysis simulator and SBML curriculum was feasible and may address gaps in massive hemoptysis management training.
Copyright © 2024 by the American Thoracic Society.
Figures
References
-
- Davidson K, Shojaee S. Managing massive hemoptysis. Chest . 2020;157:77–88. - PubMed
-
- Rowe T, Vitale K, Schroedl C, Malsin E, Argento AC.2023. apccmpd.memberclicks.net/2023_awards_annual-conference
-
- Rosenthal ME, Adachi M, Ribaudo V, Mueck JT, Schneider RF, Mayo PH. Achieving housestaff competence in emergency airway management using scenario based simulation training: comparison of attending vs housestaff trainers. Chest . 2006;129:1453–1458. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

