Huperzine A Regulates the Physiological Homeostasis of Amyloid Precursor Protein Proteolysis and Tau Protein Conformation-A Computational and Experimental Investigation
- PMID: 39056711
- PMCID: PMC11273828
- DOI: 10.3390/biology13070518
Huperzine A Regulates the Physiological Homeostasis of Amyloid Precursor Protein Proteolysis and Tau Protein Conformation-A Computational and Experimental Investigation
Abstract
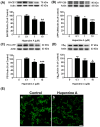
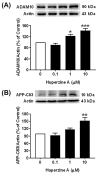
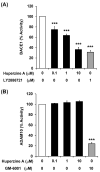
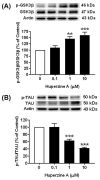
The beneficial actions of the natural compound Huperzine A (Hup A) against age-associated learning and memory deficits promote this compound as a nootropic agent. Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathophysiology is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ). Toxic Aβ oligomers account for the cognitive dysfunctions much before the pathological lesions are manifested in the brain. In the present study, we investigated the effects of Hup A on amyloid precursor protein (APP) proteolysis in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Hup A downregulated the expression of β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) and presenilin 1 (PS1) levels but augmented the levels of A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 10 (ADAM10) with significant decrement in the Aβ levels. We herein report for the first time an in silico molecular docking analysis that revealed that Hup A binds to the functionally active site of BACE1. We further analyzed the effect of Hup A on glycogen synthase kinase-3 β (GSK3β) and phosphorylation status of tau. In this scenario, based on the current observations, we propose that Hup A is a potent regulator of APP processing and capable of modulating tau homeostasis under physiological conditions holding immense potential in preventing and treating AD like disorders.
Keywords: A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 10; Alzheimer’s disease; Huperzine A; amyloid beta; amyloid precursor protein; presenilin 1; tau; β-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

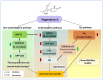
 = increase,
= increase,  = decrease).
= decrease).Similar articles
-
Huperzine A regulates amyloid precursor protein processing via protein kinase C and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells over-expressing wild type human amyloid precursor protein 695.Neuroscience. 2007 Dec 5;150(2):386-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.09.022. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17945434
-
FLZ alleviates the memory deficits in transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease via decreasing beta-amyloid production and tau hyperphosphorylation.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 4;8(11):e78033. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078033. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24223757 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin regulates the transcription of βAPP-cleaving secretases mediated through melatonin receptors in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.J Pineal Res. 2015 Oct;59(3):308-20. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12260. Epub 2015 Jul 18. J Pineal Res. 2015. PMID: 26123100
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
Development of molecular tools for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease that are based on detection of amyloidogenic proteins.Prion. 2021 Dec;15(1):56-69. doi: 10.1080/19336896.2021.1917289. Prion. 2021. PMID: 33910450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

