HSV-1 and Cellular miRNAs in CSF-Derived Exosomes as Diagnostically Relevant Biomarkers for Neuroinflammation
- PMID: 39056790
- PMCID: PMC11275151
- DOI: 10.3390/cells13141208
HSV-1 and Cellular miRNAs in CSF-Derived Exosomes as Diagnostically Relevant Biomarkers for Neuroinflammation
Abstract
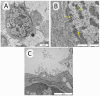
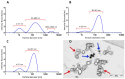
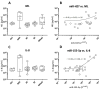
Virus-associated chronic inflammation may contribute to autoimmunity in a number of diseases. In the brain, autoimmune encephalitis appears related to fluctuating reactivation states of neurotropic viruses. In addition, viral miRNAs and proteins can be transmitted via exosomes, which constitute novel but highly relevant mediators of cellular communication. The current study questioned the role of HSV-1-encoded and host-derived miRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-derived exosomes, enriched from stress-induced neuroinflammatory diseases, mainly subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), psychiatric disorders (AF and SZ), and various other neuroinflammatory diseases. The results were compared with CSF exosomes from control donors devoid of any neuroinflammatory pathology. Serology proved positive, but variable immunity against herpesviruses in the majority of patients, except controls. Selective ultrastructural examinations identified distinct, herpesvirus-like particles in CSF-derived lymphocytes and monocytes. The likely release of extracellular vesicles and exosomes was most frequently observed from CSF monocytes. The exosomes released were structurally similar to highly purified stem-cell-derived exosomes. Exosomal RNA was quantified for HSV-1-derived miR-H2-3p, miR-H3-3p, miR-H4-3p, miR-H4-5p, miR-H6-3p, miR-H27 and host-derived miR-21-5p, miR-146a-5p, miR-155-5p, and miR-138-5p and correlated with the oxidative stress chemokine IL-8 and the axonal damage marker neurofilament light chain (NfL). Replication-associated miR-H27 correlated with neuronal damage marker NfL, and cell-derived miR-155-5p correlated with oxidative stress marker IL-8. Elevated miR-138-5p targeting HSV-1 latency-associated ICP0 inversely correlated with lower HSV-1 antibodies in CSF. In summary, miR-H27 and miR-155-5p may constitute neuroinflammatory markers for delineating frequent and fluctuating HSV-1 replication and NfL-related axonal damage in addition to the oxidative stress cytokine IL-8 in the brain. Tentatively, HSV-1 remains a relevant pathogen conditioning autoimmune processes and a psychiatric clinical phenotype.
Keywords: CSF exosomes; HSV-1; IL-8; NfL; encephalitis; low-grade inflammation; miRNA; neuronal damage; oxidative stress; psychiatric disease; traumatic brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Duncan Ross was employed by the company Kimera Labs Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wilke J.B.H., Hindermann M., Berghoff S.A., Zihsler S., Arinrad S., Ronnenberg A., Barnkothe N., Steixner-Kumar A.A., Röglin S., Stöcker W., et al. Autoantibodies against NMDA receptor 1 modify rather than cause encephalitis. Mol. Psychiatry. 2021;26:7746–7759. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01238-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schretlen D.J., Vannorsdall T.D., Winicki J.M., Mushtaq Y., Hikida T., Sawa A., Yolken R.H., Dickerson F.B., Cascella N.G. Neuroanatomic and cognitive abnormalities related to herpes simplex virus type 1 in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2010;118:224–231. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2010.01.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

