Effect of Different Graft Material Consistencies in the Treatment of Minimal Bone Dehiscence: A Retrospective Pilot Study
- PMID: 39056985
- PMCID: PMC11275297
- DOI: 10.3390/dj12070198
Effect of Different Graft Material Consistencies in the Treatment of Minimal Bone Dehiscence: A Retrospective Pilot Study
Abstract
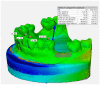
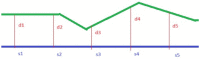
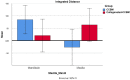
Among different therapeutic strategies proposed in the case of bone volume deficit, guided bone regeneration (GBR) is a consolidated surgical procedure. The objective of this study is to retrospectively evaluate the behavior of two bone grafts with different consistencies in the GBR procedure by measuring the volumetric tissue changes 1 year after surgery. For this retrospective analysis, 25 cases of GBR with simultaneous implant insertion were selected. A total of 13 were grafted with a porcine cortico-cancellous bone mix (CCBM group), and 12 were grafted with a pre-hydrated granulated cortico-cancellous bone mix of porcine origin blended with 20% TSV gel (Collagenated-CCBM). A collagen membrane was fixed to cover the bone defect. A total of 42 implants were placed with computer-guided surgery. Preoperative and 12-month postoperative digital impressions were used to evaluate dimensional changes. Student's t-test used for independent samples showed no statistically significant differences between the integrated distance (p = 0.995) and mean distance (p = 0.734). The mean integrated distance in the CCBM group was 41.80 (SD. 101.18) compared to a mean of 42.04 (SD. 66.71) in the Collagenated-CCBM group. Given the limitations of this study, in patients with peri-implant bone dehiscence, simple heterologous and collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone grafts are suitable for filling the bone defect to promote bone regeneration, although further studies are needed.
Keywords: bone grafts; collagen membrane; guided bone regeneration (GBR); implant insertion; volumetric tissue changes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chiapasco M., Romeo E., Casentini P., Rimondini L. Alveolar distraction osteogenesis vs. vertical guided bone regeneration for the correction of vertically deficient edentulous ridges: A 1–3-year prospective study on humans. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2004;15:82–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2004.00999.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aghaloo T.L., Moy P.K. Which hard tissue augmentation techniques are the most successful in furnishing bony support for implant placement? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2007;22:49–70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

