Emerging Strategies against Non-Typhoidal Salmonella: From Pathogenesis to Treatment
- PMID: 39057083
- PMCID: PMC11275306
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46070442
Emerging Strategies against Non-Typhoidal Salmonella: From Pathogenesis to Treatment
Abstract
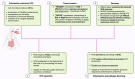
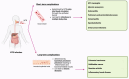
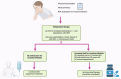
Even with the intensive efforts by public health programs to control and prevent it, non-typhoidal Salmonella (NTS) infection remains an important public health challenge. It is responsible for approximately 150 million illnesses and 60,000 deaths worldwide annually. NTS infection poses significant risks with high rates of morbidity and mortality, leading to potential short- and long-term complications. There is growing concern among health authorities about the increasing incidence of antimicrobial resistance, with multidrug resistance totaling 22.6% in Europe, highlighting an urgent need for new therapeutic approaches. Our review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of NTS infection. We outline the molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of NTS infection, as well as the events leading to invasive NTS infection and the subsequent complications associated with it. Given the widespread implications of antimicrobial resistance, our review also presents the global landscape of resistance, including multidrug resistance, and delve into the underlying mechanisms driving this resistance. The rising rates of antibiotic resistance frequently lead to treatment failures, emphasizing the importance of investigating alternative therapeutic options. Therefore, in this review we also explore potential alternative therapies that could offer promising approaches to treating NTS infections.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; diagnostic methods; iNTS; non-typhoidal Salmonella; pathogenesis; probiotics; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ghazy A., Nyarku R., Faraj R., Bentum K., Woube Y., Williams M., Alocilja E., Abebe W. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Plasmonic Detection of Escherichia Coli, Salmonella Enterica, Campylobacter Jejuni, and Listeria Monocytogenes from Bovine Fecal Samples. Microorganisms. 2024;12:1069. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061069. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nemhauser J.B., editor. CDC Yellow Book 2024: Health Information for International Travel. Oxford University Press; New York, NY, USA: 2023.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

