The RNA binding protein Arid5a drives IL-17-dependent autoantibody-induced glomerulonephritis
- PMID: 39058386
- PMCID: PMC11284280
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20240656
The RNA binding protein Arid5a drives IL-17-dependent autoantibody-induced glomerulonephritis
Abstract
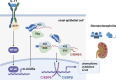
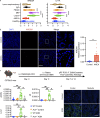
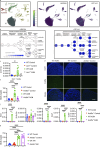
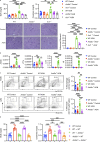
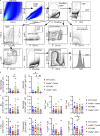
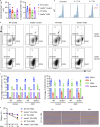
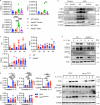
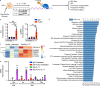
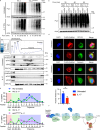
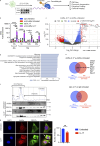
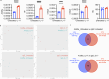
Autoantibody-mediated glomerulonephritis (AGN) arises from dysregulated renal inflammation, with urgent need for improved treatments. IL-17 is implicated in AGN and drives pathology in a kidney-intrinsic manner via renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs). Nonetheless, downstream signaling mechanisms provoking kidney pathology are poorly understood. A noncanonical RNA binding protein (RBP), Arid5a, was upregulated in human and mouse AGN. Arid5a-/- mice were refractory to AGN, with attenuated myeloid infiltration and impaired expression of IL-17-dependent cytokines and transcription factors (C/EBPβ, C/EBPδ). Transcriptome-wide RIP-Seq revealed that Arid5a inducibly interacts with conventional IL-17 target mRNAs, including CEBPB and CEBPD. Unexpectedly, many Arid5a RNA targets corresponded to translational regulation and RNA processing pathways, including rRNAs. Indeed, global protein synthesis was repressed in Arid5a-deficient cells, and C/EBPs were controlled at the level of protein rather than RNA accumulation. IL-17 prompted Arid5a nuclear export and association with 18S rRNA, a 40S ribosome constituent. Accordingly, IL-17-dependent renal autoimmunity is driven by Arid5a at the level of ribosome interactions and translation.
© 2024 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: S.L. Gaffen reported personal fees from Trotana and Aclaris Therapeutics during the conduct of the study; in addition, S.L. Gaffen had a patent number 8,460,647 issued. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures


References
-
- Amatya, N., Childs E.E., Cruz J.A., Aggor F.E.Y., Garg A.V., Berman A.J., Gudjonsson J.E., Atasoy U., and Gaffen S.L.. 2018. IL-17 integrates multiple self-reinforcing, feed-forward mechanisms through the RNA binding protein Arid5a. Sci. Signal. 11:eaat4617. 10.1126/scisignal.aat4617 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anwar, T., Sen B., Aggarwal S., Nath R., Pathak N., Katoch A., Aiyaz M., Trehanpati N., Khosla S., and Ramakrishna G.. 2018. Differentially regulated gene expression in quiescence versus senescence and identification of ARID5A as a quiescence associated marker. J. Cell. Physiol. 233:3695–3712. 10.1002/jcp.26227 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bechara, R., Amatya N., Bailey R.D., Li Y., Aggor F.E.Y., Li D.D., Jawale C.V., Coleman B.M., Dai N., Gokhale N.S., et al. . 2021. The m6A reader IMP2 directs autoimmune inflammation through an IL-17- and TNFα-dependent C/EBP transcription factor axis. Sci. Immunol. 6:eabd1287. 10.1126/sciimmunol.abd1287 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

