CHRONOS-4: phase 3 study of copanlisib plus rituximab-based immunochemotherapy in relapsed indolent B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 39058951
- PMCID: PMC11416582
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024013236
CHRONOS-4: phase 3 study of copanlisib plus rituximab-based immunochemotherapy in relapsed indolent B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
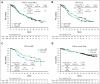
Copanlisib, a pan-class I phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor with predominant activity against the α and δ isoforms, previously demonstrated durable responses as monotherapy and improved progression-free survival (PFS) in combination with rituximab in patients with relapsed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (iNHL). CHRONOS-4 was a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to investigate the efficacy and safety of copanlisib in combination with standard immunochemotherapy in patients with relapsed iNHL. Patients (n = 524) were randomized (1:1) to copanlisib (60 mg IV) plus immunochemotherapy (rituximab and bendamustine [R-B] or placebo plus R-B). Copanlisib/placebo were administered with R-B (days 1, 8, and 15 of each 28-day cycle) for ≤6 cycles and as monotherapy from cycle 7 up to 12 months. The primary study end point was PFS. Median exposure was 8.5 months (0.2-12.9) for copanlisib plus R-B and 11.4 months (0.1-12.6) for placebo plus R-B. Median PFS was 32.9 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 24.4-38.6) for copanlisib plus R-B and 33.3 months (95% CI, 27.8-42.8) for placebo plus R-B (hazard ratio, 1.13; 95% CI, 0.88-1.44; P = .83). No differences between treatment arms were observed in overall survival (data not yet mature), objective response rate, and duration of response for the overall population or individual histology types. Overall, copanlisib plus R-B was associated with higher rates of serious treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs), grade 4 and 5 TEAEs, and treatment discontinuation. A number of serious TEAEs were infections. Overall, copanlisib plus R-B did not provide clinical benefit vs placebo plus R-B and was associated with worse tolerability in patients with relapsed iNHL. This trial was registered at www.ClinicalTrials.gov as #NCT02626455.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: P.L.Z. reports consulting fees from EUSA Pharma, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, and Novartis; speaker bureau involvement for AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), Celltrion, EUSA Pharma, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen-Cilag, Kyowa Kirin, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Roche, Servier, and Takeda; and advisory board participation for ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BMS, Celltrion, EUSA Pharma, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen-Cilag, Kyowa Kirin, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, Novartis, Roche, Sandoz, Secura Bio, Servier, and Takeda, outside the submitted work. H.W. reports travel grants from Amgen, Bayer, Pfizer, and Takeda; and research grants from Amgen, Bayer, and Pfizer, outside the submitted work. T.M.K. reports institutional support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Black Diamond Therapeutics, Blueprint Medicines, BMS, Boryung, Celgene, F. Hoffmann-La Roche/Genentech, Hanmi, Janssen, Novartis, Regeneron, Sanofi, Takeda, and Yuhan; consulting fees from AstraZeneca, IMBDx, Janssen, Regeneron, Samsung Bioepis, Takeda, and Yuhan; and advisory board participation for AstraZeneca, Janssen, Regeneron, and Takeda, outside the submitted work. M.Ö. reports research grants from AbbVie, Acerta, Bayer, Janssen, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, Pfizer, PSI, Roche, and Takeda; and travel support from AbbVie, Merck, Sharp & Dohme, and Sandoz, outside the submitted work. I.K. reports involvement in clinical trials for AbbVie, Acerta, Bayer, Cromos Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, InnoCare Pharma, Merck, MorphoSys, Pharmacyclics, and Takeda; and speaker bureau involvement for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Biopharma, Janssen, Merck, Roche, and Takeda, outside the submitted work. C.P. is an employee of Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc and may hold stock or stock options in the company. S.C. is an employee of Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc. A.W. is an employee of Bayer AG and may hold stock or stock options in the company. P.N.M. is an employee of Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc and may hold stock or stock options in the company. F.O. is an employee of Bayer SA. V.B. is an employee of Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc and may hold stock or stock options in the company. B.H.C. is an employee of Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals, Inc and may hold stock or stock options in the company. M.D. reports research grants from AbbVie, Bayer, BMS/Celgene, Gilead/Kite, Janssen, Lilly, and Roche; honoraria from AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Gilead/Kite, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, and Roche; and advisory board participation for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BMS/Celgene, Gilead/Kite, Janssen, Lilly/Loxo Oncology, Novartis, and Roche, outside the submitted work. M.M. reports research grants from Bayer, Genentech, GM Biosciences, ImmunoVaccine Technologies, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, Roche, and Seattle Genetics; honoraria from ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BMS, Celgene, Epizyme, ImmunoVaccine Technologies, Janssen, Kite, Pharmacyclics, Regeneron, Roche, Seagen, Seattle Genetics, and Takeda; stipends from ADC Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, BMS, Celgene, Epizyme, ImmunoVaccine Technologies, Kite, Regeneron, and Seagen; consultancy for Bayer, Genentech, Juno Therapeutics, Roche, Seattle Genetics, Takeda, and Teva; membership on board/advisory committee for Genentech and Merck; and equity ownership in Merck, outside the submitted work. P.G. reports consulting fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, and Daiichi Sankyo; and research grants from Kite, outside the submitted work. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Dreyling M, Ghielmini M, Rule S, et al. Newly diagnosed and relapsed follicular lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(3):298–308. - PubMed
-
- Dreyling M, Santoro A, Mollica L, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition by copanlisib in relapsed or refractory indolent lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(35):3898–3905. - PubMed
-
- US Food and Drug Administration FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Copanlisib for Relapsed Follicular Lymphoma. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grant...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

