Hodgkin lymphoma involving the extra-axial CNS: an AHOD1331, PHL-C1, and PHL-C2 report from the COG and EuroNet-PHL
- PMID: 39058968
- PMCID: PMC11416590
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023012346
Hodgkin lymphoma involving the extra-axial CNS: an AHOD1331, PHL-C1, and PHL-C2 report from the COG and EuroNet-PHL
Abstract
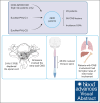
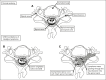
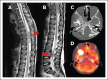
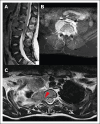
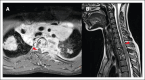
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) involving the central nervous system (CNS) is exceedingly rare. Information regarding the presentation, management, treatment, and outcome of patients with CNS HL is limited to case reports or small series. We describe 45 pediatric patients with 55 extra-axial CNS lesions at diagnosis with HL from a cohort of 4995 patients enrolled on Children's Oncology Group AHOD1331 and the European Network for Pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma C1 and C2 trials, with an overall incidence of 0.9%. Up to 82.2% of patients had a single CNS lesion in the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral spine. In the evaluated cohort, HL did not occur within the CNS parenchyma. Lesions extended into the extra-axial CNS space from adjacent soft tissue or bone and never directly infiltrated through the dura into the brain or spinal cord. Patients with CNS involvement had a twofold greater incidence of extranodal lesions than previously reported cohorts without CNS involvement. After 2 cycles of chemotherapy, 89.1% of CNS lesions demonstrated a complete metabolic response and >75% decrease in volume. Thirteen CNS lesions (23.6%) received irradiation; none were sites of disease relapse. Relapse occurred at the site of 2 lesions involving the CNS, both of which had an adequate interim response to chemotherapy. In summary, we present, to our knowledge, the largest reported cohort of systemic HL involving the CNS at diagnosis, demonstrating that these lesions originate from surrounding tissues, extend into the extra-axial CNS space, and respond similarly to other nodal and extranodal disease. The trials were registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02166463, #NCT00433459, and #NCT02684708.
© 2024 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: K.M.K., J.F., and S.M.C. served on a scientific advisory board for Seagen. C.M.-K. has received institutional research funding from Merck on a joint clinical trial research project. H.L. is a consultant for Innervate Radiopharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- National Cancer Institute. SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Hodgkin Lymphoma. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/hodg.html
-
- Deutsches Kinderkrebsregister German Childhood Cancer Registry Annual Report 2019. https://www.kinderkrebsregister.de/dkkr/ergebnisse/jahresberichte/jahres...
-
- Englund A, Glimelius I, Rostgaard K, et al. Hodgkin lymphoma in children, adolescents and young adults - a comparative study of clinical presentation and treatment outcome. Acta Oncol. 2018;57(2):276–282. - PubMed
-
- Hagleitner MM, Metzger ML, Flerlage JE, et al. Liver involvement in pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma: a systematic review by an international collaboration on Staging Evaluation and Response Criteria Harmonization (SEARCH) for Children, Adolescent, and Young Adult Hodgkin Lymphoma (CAYAHL) Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020;67(8) - PubMed
-
- Lewis J, McCarten K, Kurch L, et al. Definition of cortical bone involvement in the staging of newly diagnosed pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma: a report from the International Working Group on Staging Evaluation and Response Criteria Harmonization (SEARCH) Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2020;67(4) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

