CYYR1 promotes the degradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 and is associated with favorable prognosis in breast cancer
- PMID: 39059493
- PMCID: PMC11399591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107601
CYYR1 promotes the degradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 and is associated with favorable prognosis in breast cancer
Abstract
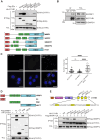
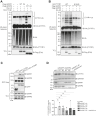
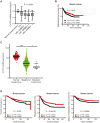
Ubiquitination plays a crucial role in cellular homeostasis by regulating the degradation, localization, and activity of proteins, ensuring proper cell function and balance. Among E3 ubiquitin ligases, WW domain-containing protein 1 (WWP1) is implicated in cell proliferation, survival, and apoptosis. Notably WWP1 is frequently amplified in breast cancer and associated with poor prognosis. Here, we identify the protein cysteine and tyrosine-rich protein 1 (CYYR1) that had previously no assigned function, as a regulator of WWP1 activity and stability. We show that CYYR1 binds to the WW domains of the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 through its PPxY motifs. This interaction triggers K63-linked autoubiquitination and subsequent degradation of WWP1. We furthermore demonstrate that CYYR1 localizes to late endosomal vesicles and directs polyubiquitinated WWP1 toward lysosomal degradation through binding to ANKyrin repeat domain-containing protein 13 A (ANKRD13A). Moreover, we found that CYYR1 expression attenuates breast cancer cell growth in anchorage-dependent and independent colony formation assays in a PPxY-dependent manner. Finally, we highlight that CYYR1 expression is significantly decreased in breast cancer and is associated with beneficial clinical outcome. Taken together our study suggests tumor suppressor properties for CYYR1 through regulation of WWP1 autoubiquitination and lysosomal degradation.
Keywords: CYYR1; E3 ubiquitin ligase; WWP1; breast cancer; ubiquitination.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

