Losartan Treatment Reduces Esophageal Eosinophilic Inflammation in a Subset of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- PMID: 39059581
- PMCID: PMC11552403
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaip.2024.07.011
Losartan Treatment Reduces Esophageal Eosinophilic Inflammation in a Subset of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
Background: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, food antigen-driven esophageal disorder. Connective tissue disorders (CTDs) and esophageal connective tissue alterations are associated with EoE. Therefore, angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade with losartan, an accepted CTD treatment, is a potential EoE treatment.
Objective: We evaluated losartan's effects on esophageal pathology, symptoms, and safety in patients with EoE with and without a CTD in an open-label, non-placebo controlled multisite study.
Methods: Fifteen participants with EoE, aged 5 to 23 years, underwent treatment with per-protocol titrated doses of losartan in an open-label, 16-week pilot trial. Losartan was added to standard of care therapy and 14 patients completed the study. Eosinophil counts served as the primary end point, whereas we also assessed the EoE Histology Scoring System, Endoscopic Reference Scores, EoE Diagnostic Panel, and patient-reported outcomes.
Results: Esophageal eosinophilia was not reduced after losartan. The peak eosinophil count was not reduced for the proximal (median [interquartile range]: -3 [-22 to 3]; P = .49) and distal esophagus (median [interquartile range]: -18 [-39 to -1]; P = .23). There were no differences in losartan response in EoE with or without CTD (n = 7 and 8, respectively). Regardless, in a small subset of four participants esophageal eosinophilia was resolved with a concomitant reduction in EoE Histology Scoring System score and Endoscopic Reference Score. Across all subjects, the Pediatric EoE Symptom Score, Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory EoE Module, and EoE Diagnostic Panel improved after losartan (P < .05).
Conclusions: Losartan treatment was associated with improved patient-reported outcome scores and EoE Diagnostic Panel biomarkers although without a reduction in esophageal eosinophilia overall. A subset of patients demonstrated improved histopathologic and endoscopic features that could not be tied to a specific feature predicting response to treatment.
Keywords: Eosinophilic esophagitis; Esophageal transcriptome; Losartan; Quality of life; Symptom scores.
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest:
JPA received payment or honoraria for lectures from Takeda Global Research and Development, participated on a Data Safety Monitoring Board for OctaPharma USA, Inc., and received grants or contracts from Cures Within Reach and Celgene.
AKRS’s co-authorship of this publication does not necessarily constitute endorsement by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institutes of Health or any other agency of the United States government.
IH received research funding from Adare/Ellodi, Allakos, Pfizer/Arena, AstraZeneca, Meritage, Celgene/Receptos/BMS, Regeneron, Shire/Takeda and is a consultant for Abbvie, Adare/Ellodi, Allakos, Amgen, Arena, AstraZeneca, Calyx/Parexel, Celgene/Receptos/BMS, Eli Lilly, EsoCap, Gossamer Bio, Parexel/Calyx, Phathom, Regeneron/Sanofi, Shire/Takeda),), and received educational speaker fees from Sanofi/Genzyme and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
TS is coinventor of patents for the EG Diagnostic Panel owned by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center
VAM has received consulting fees from Phathom, Regeneron, Sanofi, and Shire (a subsidiary of Takeda); has received honorarium for lectures from the American Gastroenterological Association; and serves on an adjudication board for Alladapt.
MHC is a consultant for Allakos, Arena Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Calypso Biotech, EsoCap Biotech, GlaxoSmithKline, Receptos/Celgene/BMS, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Robarts Clinical Trials, Inc/Alimentiv, Inc, and Shire (a Takeda company).
KEC is currently employed by and has an equity interest in Alnylam.
SSA received consultant fees from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, and Bristol Myers Squibb; received research funding from Implicit Biosciences; is coinventor of oral viscous budesonide University of California, San Diego patent Takeda license; and received educational speaker fees from Sanofi/Genzyme and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
MER is a consultant for Pulm One, Spoon Guru, ClostraBio, Serpin Pharm, Allakos, Celldex, Nexstone One, Santa Ana Bio, EnZen Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Astra Zeneca, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Regeneron/Sanofi, Revolo Biotherapeutics, and Guidepoint and has an equity interest in the first nine listed, and royalties from reslizumab (Teva Pharmaceuticals), PEESSv2 (Mapi Research Trust) and UpToDate. M.E.R. is an inventor of patents owned by Cincinnati Children’s Hospital.
The remaining authors declare that they have no relevant conflicts of interest.
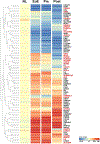
Figures





References
-
- Aceves SS, Newbury RO, Dohil R, Bastian JF, Broide DH. Esophageal remodeling in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2007;119:206–12. - PubMed
-
- Aceves SS, Chen D, Newbury RO, Dohil R, Bastian JF, Broide DH. Mast cells infiltrate the esophageal smooth muscle in patients with eosinophilic esophagitis, express TGF-β1, and increase esophageal smooth muscle contraction. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010;126:1198–204.e4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

