Non-equilibrium transport in polymer mixed ionic-electronic conductors at ultrahigh charge densities
- PMID: 39060469
- PMCID: PMC11599050
- DOI: 10.1038/s41563-024-01953-6
Non-equilibrium transport in polymer mixed ionic-electronic conductors at ultrahigh charge densities
Abstract
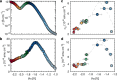
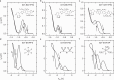
Conducting polymers are mixed ionic-electronic conductors that are emerging candidates for neuromorphic computing, bioelectronics and thermoelectrics. However, fundamental aspects of their many-body correlated electron-ion transport physics remain poorly understood. Here we show that in p-type organic electrochemical transistors it is possible to remove all of the electrons from the valence band and even access deeper bands without degradation. By adding a second, field-effect gate electrode, additional electrons or holes can be injected at set doping states. Under conditions where the counterions are unable to equilibrate in response to field-induced changes in the electronic carrier density, we observe surprising, non-equilibrium transport signatures that provide unique insights into the interaction-driven formation of a frozen, soft Coulomb gap in the density of states. Our work identifies new strategies for substantially enhancing the transport properties of conducting polymers by exploiting non-equilibrium states in the coupled system of electronic charges and counterions.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: D.H.L.T., X.R., I.E.J., T.B.E.M., T.G.M., L.Z. and H.S. have submitted a patent application based on the findings of this study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures













References
-
- Dugdale, J. S. The Electrical Properties of Disordered Metals (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1995).
-
- Efros, A. & Skhlovskii, B. Coulomb gap and low temperature conductivity of disordered systems. J. Phys. C8, L49–L51 (1975).
-
- Koopmans, M. & Koster, L. J. A. Carrier–carrier Coulomb interactions reduce power factor in organic thermoelectrics. Appl. Phys. Lett.119, 143301 (2021).
-
- Xu, K. et al. On the origin of Seebeck coefficient inversion in highly doped conducting polymers. Adv. Funct. Mater.32, 2112276 (2022).
-
- Yoon, C., Reghu, M., Moses, D. & Heeger, A. Characteristic temperature dependence of resistivity in PPy(PF6) near the metal–insulator transition. Synth. Met.69, 369–370 (1995).
Grants and funding
- 101020872/EC | EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020 | H2020 Priority Excellent Science | H2020 European Research Council (H2020 Excellent Science - European Research Council)
- 101020872/EC | EC Seventh Framework Programm | FP7 Ideas: European Research Council (FP7-IDEAS-ERC - Specific Programme: "Ideas" Implementing the Seventh Framework Programme of the European Community for Research, Technological Development and Demonstration Activities (2007 to 2013))
- ANR-21-CE24-0004-01/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- EP/W017091/RCUK | Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

