Crosstalk between bone and the immune system
- PMID: 39060500
- PMCID: PMC11415469
- DOI: 10.1007/s00774-024-01539-x
Crosstalk between bone and the immune system
Erratum in
-
Correction: Crosstalk between bone and the immune system.J Bone Miner Metab. 2024 Jul;42(4):481-482. doi: 10.1007/s00774-024-01547-x. J Bone Miner Metab. 2024. PMID: 39251416 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
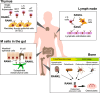
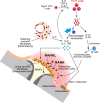
Bone functions not only as a critical element of the musculoskeletal system but also serves as the primary lymphoid organ harboring hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and immune progenitor cells. The interdisciplinary field of osteoimmunology has illuminated the dynamic interactions between the skeletal and immune systems, vital for the maintenance of skeletal tissue homeostasis and the pathogenesis of immune and skeletal diseases. Aberrant immune activation stimulates bone cells such as osteoclasts and osteoblasts, disturbing the bone remodeling and leading to skeletal disorders as seen in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. On the other hand, intricate multicellular network within the bone marrow creates a specialized microenvironment essential for the maintenance and differentiation of HSCs and the progeny. Dysregulation of immune-bone crosstalk in the bone marrow environment can trigger tumorigenesis and exacerbated inflammation. A comprehensive deciphering of the complex "immune-bone crosstalk" leads to a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of immune diseases as well as skeletal diseases, and might provide insight into potential therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Bone; Bone marrow microenvironment; Immune system; Osteoclast; Osteoimmunology; RANKL.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The Department of Osteoimmunology is an endowment department, supported with unrestricted grants from AYUMI Pharmaceutical Corporation, ELECOM, JCR Pharmaceuticals, Kondo Cotton Spinning, Meiji, MIKIHOUSE, MITSUI FUDOSAN, Noevir, TAKENAKA, TENNENBUTSU IKAGAKU KENKYU ZAIDAN and Yakult.
Figures

References
-
- Okamoto K, Nakashima T, Shinohara M, Negishi-Koga T, Komatsu N, Terashima A, Sawa S, Nitta T, Takayanagi H (2017) Osteoimmunology: the conceptual framework unifying the immune and skeletal systems. Physiol Rev 97:1295–1349 - PubMed
-
- Takayanagi H, Ogasawara K, Hida S, Chiba T, Murata S, Sato K, Takaoka A, Yokochi T, Oda H, Tanaka K, Nakamura K, Taniguchi T (2000) T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-γ. Nature 408:600–605 - PubMed
-
- Sugiyama T, Omatsu Y, Nagasawa T (2019) Niches for hematopoietic stem cells and immune cell progenitors. Int Immunol 31:5–11 - PubMed
-
- Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ, Dunstan CR et al (1998) Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 93:165–176 - PubMed
-
- Yasuda H, Shima N, Nakagawa N, Yamaguchi K, Kinosaki M, Mochizuki S, Tomoyasu A, Yano K, Goto M, Murakami A, Tsuda E, Morinaga T, Higashio K, Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Suda T (1998) Osteoclast differentiation factor is a ligand for osteoprotegerin/osteoclastogenesis-inhibitory factor and is identical to TRANCE/RANKL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:3597–3602 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

