Novel hypoxia-induced HIF-1αactivation in asthma pathogenesis
- PMID: 39061007
- PMCID: PMC11282634
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-024-02869-0
Novel hypoxia-induced HIF-1αactivation in asthma pathogenesis
Abstract
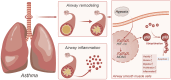
Background: Asthma's complexity, marked by airway inflammation and remodeling, is influenced by hypoxic conditions. This study focuses on the role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1α) and P53 ubiquitination in asthma exacerbation.
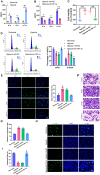
Methods: High-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics were used to identify genes associated with asthma progression, with an emphasis on GO and KEGG pathway analyses. An asthma mouse model was developed, and airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs) were isolated to create an in vitro hypoxia model. Cell viability, proliferation, migration, and apoptosis were assessed, along with ELISA and Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining.
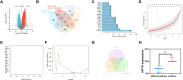
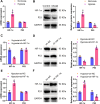
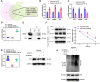
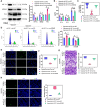
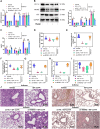
Results: A notable increase in HIF-1α was observed in both in vivo and in vitro asthma models. HIF-1α upregulation enhanced ASMCs' viability, proliferation, and migration, while reducing apoptosis, primarily via the promotion of P53 ubiquitination through MDM2. In vivo studies showed increased inflammatory cell infiltration and airway structural changes, which were mitigated by the inhibitor IDF-11,774.
Conclusion: The study highlights the critical role of the HIF-1α-MDM2-P53 axis in asthma, suggesting its potential as a target for therapeutic interventions. The findings indicate that modulating this pathway could offer new avenues for treating the complex respiratory disorder of asthma.
Keywords: Airway Remodeling; Asthma; HIF-1α; Hypoxia; P53 ubiquitination.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wechsler ME, Munitz A, Ackerman SJ, et al. Eosinophils in Health and Disease: a state-of-the-art review. Mayo Clin Proc. 2021;96(10):2694–707. 10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.04.025. - PubMed
-
- Banno A, Reddy AT, Lakshmi SP, Reddy RC. Bidirectional interaction of airway epithelial remodeling and inflammation in asthma. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020;134(9):1063–79. 10.1042/CS20191309. - PubMed
-
- Elieh Ali Komi D, Bjermer L. Mast cell-mediated Orchestration of the Immune responses in human allergic asthma: current insights. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2019;56(2):234–47. 10.1007/s12016-018-8720-1. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

