The surgical interval between robot-assisted SEEG and epilepsy resection surgery is an influencing factor of SSI
- PMID: 39061108
- PMCID: PMC11282661
- DOI: 10.1186/s13756-024-01438-w
The surgical interval between robot-assisted SEEG and epilepsy resection surgery is an influencing factor of SSI
Abstract
Background: In recent years, the development of robotic neurosurgery has brought many benefits to patients, but there are few studies on the occurrence of surgical site infection (SSI) after robot-assisted stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG). The purpose of this study was to collect relevant data from robot-assisted SEEG over the past ten years and to analyze the influencing factors and economic burden of surgical site infection.
Methods: Basic and surgical information was collected for all patients who underwent robot-assisted SEEG from January 2014 to December 2023. Logistic regression was used to analyze the factors influencing SSI according to different subgroups (radiofrequency thermocoagulation or epilepsy resection surgery).
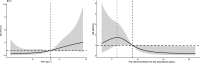
Results: A total of 242 subjects were included in this study. The risk of SSI in the epilepsy resection surgery group (18.1%) was 3.5 times greater than that in the radiofrequency thermocoagulation group (5.1%) (OR 3.49, 95% CI 1.39 to 9.05); this difference was statistically significant. SSI rates in the epilepsy resection surgery group were associated with shorter surgical intervals (≤ 9 days) and higher BMI (≥ 23 kg/m2) (6.1 and 5.2 times greater than those in the control group, respectively). Hypertension and admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) were risk factors for SSI in the radiofrequency thermocoagulation group. Patients with SSIs had $21,231 more total hospital costs, a 7-day longer hospital stay, and an 8-day longer postoperative hospital stay than patients without SSI.
Conclusions: The incidence of SSI in patients undergoing epilepsy resection after stereoelectroencephalography was higher than that in patients undergoing radiofrequency thermocoagulation. For patients undergoing epilepsy resection surgery, prolonging the interval between stereoelectroencephalography and epilepsy resection surgery can reduce the risk of SSI; At the same time, for patients receiving radiofrequency thermocoagulation treatment, it is not recommended to enter the ICU for short-term observation if the condition permits.
Keywords: Epilepsy resection surgery; Radiofrequency thermocoagulation; Stereoelectroencephalography; Surgical site infection.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Li P, Zhou Y, Zhang Q, Yang Y, Wang M, Zhu R, et al. Frameless robot-assisted stereoelectroencephalography-guided radiofrequency: methodology, results, complications and stereotactic application accuracy in pediatric hypothalamic hamartomas. Front Neurol. 2023. 10.3389/fneur.2023.1259171. 10.3389/fneur.2023.1259171 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous