The Multifaceted Role of Neutrophils in NSCLC in the Era of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- PMID: 39061147
- PMCID: PMC11274601
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16142507
The Multifaceted Role of Neutrophils in NSCLC in the Era of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Abstract
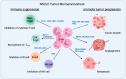
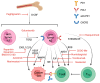
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer-related death in both males and females in the U.S. and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 85%. Although the use of first- or second-line immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) exhibits remarkable clinical benefits, resistance to ICIs develops over time and dampens the efficacy of ICIs in patients. Tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs) have an important role in modulating the tumor microenvironment (TME) and tumor immune response. The major challenge in the field is to characterize the TANs in NSCLC TME and understand the link between TAN-related immunosuppression with ICI treatment response. In this review, we summarize the current studies of neutrophil interaction with malignant cells, T-cells, and other components in the TME. Ongoing clinical trials are aimed at utilizing reagents that have putative effects on tumor-associated neutrophils, in combination with ICI. Elevated neutrophil populations and neutrophil-associated factors could be potential therapeutic targets to enhance anti-PD1 treatment in NSCLC.
Keywords: immunotherapy; neutrophils; non-small-cell lung cancer; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
D.L.G. reports honoraria for scientific advisory boards from AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Alethia Biotherapeutics, Menarini Richerche, Eli Lilly, 4D Pharma, and Onconova and research support from Janssen, Takeda, Astellas, Ribon Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Mirati Therapeutics, and AstraZeneca. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Jain A.S., Prasad A., Pradeep S., Dharmashekar C., Achar R.R., Ekaterina S., Victor S., Amachawadi R.G., Prasad S.K., Pruthvish R., et al. Everything Old Is New Again: Drug Repurposing Approach for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Targeting MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021;11:741326. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.741326. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

