Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN): A Narrative Review and Proposed Theoretical Model
- PMID: 39061210
- PMCID: PMC11274737
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16142571
Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN): A Narrative Review and Proposed Theoretical Model
Abstract
Background: Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a common and debilitating symptom experienced by cancer survivors. Despite the burden of CIPN-related symptoms, interventions remain limited.
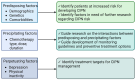
Objectives: This narrative review seeks to propose a framework for CIPN predisposing, precipitating, and perpetuating factors (3Ps), which will provide a foundation for future research and clinical interventions aimed at mitigating CIPN-related symptoms and morbidity.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search was performed using PubMed, guided by keywords related to "chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy." Studies were limited to those with full text available in English.
Results: Predisposing factors outlined in this framework, such as older age and comorbid conditions, can be used to identify patients who have a higher risk of developing CIPN. The major precipitating factor of CIPN is the delivery of chemotherapy to peripheral nerves, which may be mitigated via cryotherapy or compression therapy during chemotherapy. Perpetuating factors can offer insight into psychological, cognitive, and behavioral modifications that could be treatment targets for CIPN management.
Conclusion: The proposed 3P model can guide the development of effective interventions for CIPN by suggesting modifiable psychological and behavioral treatment targets that may mitigate the impact of CIPN for cancer patients.
Keywords: cancer survivorship; chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy; theoretical model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hershman D.L., Lacchetti C., Dworkin R.H., Lavoie Smith E.M., Bleeker J., Cavaletti G., Chauhan C., Gavin P., Lavino A., Lustberg M.B., et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014;32:1941–1967. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2013.54.0914. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Marshall T.F., Zipp G.P., Battaglia F., Moss R., Bryan S. Chemotherapy-induced-peripheral neuropathy, gait and fall risk in older adults following cancer treatment. J. Cancer Res. Pract. 2017;4:134–138. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrpr.2017.03.005. - DOI
-
- Hershman D.L., Weimer L.H., Wang A., Kranwinkel G., Brafman L., Fuentes D., Awad D., Crew K.D. Association between patient reported outcomes and quantitative sensory tests for measuring long-term neurotoxicity in breast cancer survivors treated with adjuvant paclitaxel chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011;125:767–774. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-1278-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources