Mutations in embB 406 Are Associated with Low-Level Ethambutol Resistance in Canadian Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates
- PMID: 39061306
- PMCID: PMC11273804
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13070624
Mutations in embB 406 Are Associated with Low-Level Ethambutol Resistance in Canadian Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates
Abstract
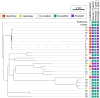
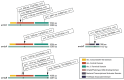
In Mycobacterium tuberculosis, molecular predictions of ethambutol resistance rely primarily on the detection of mutations within embB. However, discordance between embB406 mutations and gold standard phenotypic drug sensitivity testing (DST) questions the significance of embB406 mutations used in molecular DST. This study tabulates embB mutations found in Canadian M. tuberculosis isolates and evaluates the impact of specific mutations on ethambutol resistance. The National Reference Centre for Mycobacteriology culture collection (n = 2796) was screened for isolates with embB mutations. Phenotypic DST was performed on the BACTEC™ MGIT™ 960 at ethambutol concentrations of 2-5 μg/mL. Whole genome sequencing was used for drug resistance predictions, phylogenomics and single nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Detection of resistance-associated embB mutations corresponded to a positive predictive value of 64.3%, negative predictive value of 99.2%, 98.7% specificity, and 73.3% sensitivity compared to phenotypic DST. Two embB406 mutation subtypes (Gly406Asp, Gly406Ala) were found among 16 isolates, of which 12 were sensitive at 5 µg/mL ethambutol with variable resistance between 2-4 µg/mL. A novel frameshift mutation in regulator embR (Gln258fs) was found in nine isolates. Mutations in embB406 were associated with low-level ethambutol resistance undetectable at the recommended critical concentration (5 μg/mL). These novel mutations may exacerbate variability in ethambutol resistance.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; embB; ethambutol; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. [(accessed on 29 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globa....
-
- Long R., Avendano M., Kunimoto D. Canadian Tuberculosis Standards. 7th ed. Public Health Agency of Canada; Ottawa, ON, Canada: 2014. Chapter 8: Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis; pp. 1–38.
-
- Brode S.K., Dwilow R., Kunimoto D., Menzies D., Khan F.A. Chapter 8: Drug-resistant tuberculosis. Can. J. Respir. Crit. Care Sleep Med. 2022;6:109–128. doi: 10.1080/24745332.2022.2039499. - DOI
-
- Public Health Agency of Canada, Tuberculosis in Canada: Infographic (2022) [(accessed on 22 May 2024)]. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/diseases-co....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

