What Place Is There for Long-Acting Antibiotics in the Management of Gram-Positive Infections? A Qualitative Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39061326
- PMCID: PMC11274069
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics13070644
What Place Is There for Long-Acting Antibiotics in the Management of Gram-Positive Infections? A Qualitative Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
Objectives: To identify the current practices with long half-life lipoglycopeptides (LGPs) and potential use/position of oritavancin.
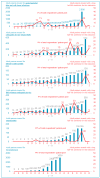
Results: Despite their indication being limited to skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), long half-life lipoglycopeptides are mainly used off-label to treat bone and joint infections (BJIs) and infective endocarditis. Oritavancin and dalbavancin are both semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide antibiotics with activity against Gram-positive organisms. The game-changing property of these two antibiotics is their one-time dosing. Due to its shorter half-life, oritavancin might have an advantage over dalbavancin for a treatment duration of less than 2 weeks, as it could be used both in prolonged treatments of complicated patients in BJIs or administered as a single-dose treatment for Gram-positive cocci infections usually treated by a 5- to 10-day antibiotic course. These infections include urinary tract infections, bacteremias, catheter-related infections, etc. In addition to the possibility of being used as an end-of-treatment injection, oritavancin could be used as an empiric therapy treatment in the postoperative period in the context of device-associated especially prosthetic joint infections to allow for the early discharge of the patient.
Methods: A qualitative survey was conducted in March 2022 including sixteen infectiologists, one internist, five hospital pharmacists, and one pharmacologist.
Conclusion: Long half-life lipoglycopeptides contribute to changing the paradigm in the management of acute bacterial infections, as infectiologists now consider a range of indications and patient profiles for one single drug. Oritavancin strengthens the therapeutic arsenal in numerous infections from BJIs to urinary tract infections and could help to manage specific clinical situations, on top of providing potential benefits for the hospital's budget.
Keywords: Gram-positive; acute bacterial infections; hospital discharge; long half-life lipoglycopeptides; long-acting antibiotics; oritavancin.
Conflict of interest statement
Aurélien Dinh has received a speaker honorarium from Menarini, MSD, Shionogi, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Johan Courjon has received a speaker honorarium from Advanz Pharma, and Menarini. Guillaume Béraud has received a speaker honorarium from Menarini, Pfizer, Gilead, MSD, GSK, and AdvanzPharma. Yann Le Goff has no conflicts of interest to report. Nicolas Kader Ettahar has received a speaker honorarium from Menarini. Matthieu Grégoire has received a speaker honorarium from Menarini, Shionogi, AdvanzPharma, Gilead, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, and Viiv. Eric Senneville has received a speaker honorarium from Menarini, MSD, Shionogi, Pfizer, Sanofi, Debiopharm, and AdvanzPharma.
Figures
References
-
- Rubino C.M., Bhavnani S.M., Moeck G., Bellibas S.E., Ambrose P.G. Population pharmacokinetic analysis for a single 1,200-milligram dose of oritavancin using data from two pivotal phase 3 clinical trials. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015;59:3365–3372. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00176-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dunbar L.M., Milata J., McClure T., Wasilewski M.M., The SIMPLIFI Study Team Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Oritavancin Front-Loaded Dosing Regimens to Daily Dosing: An Analysis of the SIMPLIFI Trial. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011;55:3476–3484. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00029-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources