Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Action Naming in Aphasia Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39061405
- PMCID: PMC11275163
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14070665
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Action Naming in Aphasia Rehabilitation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
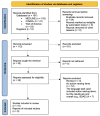
Anomia, characterized by difficulty in word retrieval, particularly action verbs, poses a significant challenge in post-stroke aphasia. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has gained attention for language processing investigations and interventions. This systematic review explores the potential of rTMS as a modality to address action-verb deficits in post-stroke aphasia. We searched MEDLINE via PubMed, CINAHL via Ebsco and Web of Science in February 2024 for English articles (1996-2024). Eligible studies involved post-stroke aphasia action naming rehabilitation with rTMS. In some of these studies, rTMS was combined with speech-language therapy. In total, 10 studies were included in this systematic review. These articles highlight the potential of rTMS in improving verb retrieval deficits. While significant improvements may not be evident, notable progress both before and after intervention is observed in this review. However, it also underscores the need for further research to enhance language recovery for individuals with post-stroke aphasia.
Keywords: action naming; aphasia; rTMS; rehabilitation; speech therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Alexander M.P., Hillis A.E. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Volume 88. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2008. Chapter 14 Aphasia; pp. 287–309. - PubMed
-
- Nickels L. Therapy for Naming Disorders: Revisiting, Revising, and Reviewing. Aphasiology. 2002;16:935–979. doi: 10.1080/02687030244000563. - DOI
-
- Conroy P., Sage K., Lambon Ralph M.A. Towards Theory-driven Therapies for Aphasic Verb Impairments: A Review of Current Theory and Practice. Aphasiology. 2006;20:1159–1185. doi: 10.1080/02687030600792009. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

