MRI-Based Inner Ear Assessment and Cochlin Tomoprotein-Based Evaluation of Perilymphatic Fistula in Patients with Sudden Hearing Loss
- PMID: 39061421
- PMCID: PMC11275193
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14070681
MRI-Based Inner Ear Assessment and Cochlin Tomoprotein-Based Evaluation of Perilymphatic Fistula in Patients with Sudden Hearing Loss
Abstract
Objectives: To study the correlation between positive cochlin tomoprotein testing (CTP), magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, and the auditory and vestibular function amongst patients with sudden hearing loss.
Study design: Prospective case series.
Methods: We prospectively examined eight patients who presented with sudden hearing loss (>60 dB) with or without vertigo or tinnitus. We performed an ELISA-based CTP detection test using middle ear lavage samples. In addition to the CTP examination, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination was performed using different sequences (T1 and a T1 sequence with a contrast medium (CM), a T2 sequence, 4 h delayed intravenous gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (3D FLAIR)).
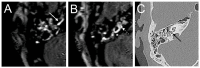
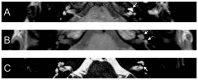
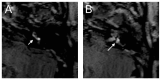
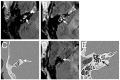
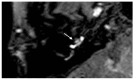
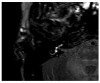
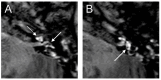
Results: All patients with sudden hearing loss (>60 dB) presented a non-specific contrast enhancement in the cochlea and vestibulum on the affected side on delayed 3D-FLAIR MRI. Four patients had a positive CTP test, suggesting a perilymphatic fistula (PLF). However, no specific MRI signal for a PLF was observed.
Conclusions: Using multimodal diagnostic measures, such as CTP testing and different MRI sequences, no correlation could be found in patients with a PLF.
Keywords: 4 h delayed intravenous gadolinium-enhanced 3D FLAIR MRI; cochlin tomoprotein; magnetic resonance imaging; perilymphatic fistula; sudden hearing loss.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bachmann-Harildstad G., Stenklev N.C., Myrvoll E., Jablonski G., Klingenberg O.J.O. β-Trace protein as a diagnostic marker for perilymphatic fluid fistula: A prospective controlled pilot study to test a sample collection technique. Otol. Neurotol. 2011;32:7–10. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3181fc74d0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Friedland D.R., Wackym P.A. A critical appraisal of spontaneous perilymphatic fistulas of the inner ear. Am. J. Otol. 1999;20:261–279. - PubMed
-
- Gibson W.P. Spontaneous perilymphatic fistula: Electrophysiologic findings in animals and man. Am. J. Otol. 1993;14:273–277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

