Can Occupational Safety and Health Preventive Measures Taken by the Employer Influence Sleep Disturbances in Teleworkers? Results from the Quantitative Study on Working Life with COVID-19 in Latvia
- PMID: 39061424
- PMCID: PMC11275139
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci14070684
Can Occupational Safety and Health Preventive Measures Taken by the Employer Influence Sleep Disturbances in Teleworkers? Results from the Quantitative Study on Working Life with COVID-19 in Latvia
Abstract
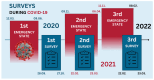
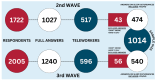
This research on sleep disturbances emerged during the COVID-19 pandemic. Our study investigated the association between self-reported sleep disturbances among teleworkers and the preventive measures employers took to improve their working environment. Answers obtained via a web survey gathered from 1086 teleworkers (517 in the spring of 2021 and 569 in the spring of 2022) were analysed. The odds of self-reported sleep disturbances were significantly higher for all preventive measures in the group of respondents reporting a lack of a particular measure. The highest odds ratios were observed for the statement "My employer identified conditions where I am teleworking" (adjusted OR = 2.98, 95% CI 2.10-4.23) and "Online team-building events were organised" (adjusted OR = 2.85, 95% CI 1.88-4.35). The results of our study have revealed that workplace interventions that serve as a mediator for sleep disorders, even if they are not directly targeted at managing sleep disturbances or stress, can reduce the number of teleworkers reporting sleep disturbances. According to our knowledge, this is the first study reporting the effectiveness of employer interventions that help teleworkers manage their sleep disturbances.
Keywords: distance work; occupational health and safety; quality; sleep; sleep disturbances; telework.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Teleworking Is Significantly Associated with Anxiety Symptoms and Sleep Disturbances among Paid Workers in the COVID-19 Era.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 13;20(2):1488. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20021488. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36674241 Free PMC article.
-
Transition to the forced telework - a challenge for trade unions identified by the study on working life with COVID-19 in Latvia.Work. 2022;71(3):527-537. doi: 10.3233/WOR-211042. Work. 2022. PMID: 35253714 Free PMC article.
-
Anticipated health effects and proposed countermeasures following the immediate introduction of telework in response to the spread of COVID-19: The findings of a rapid health impact assessment in Japan.J Occup Health. 2021 Jan;63(1):e12198. doi: 10.1002/1348-9585.12198. J Occup Health. 2021. PMID: 33527667 Free PMC article.
-
Musculoskeletal pain and risk factors in office workers versus teleworkers: A systematic review.Work. 2025 Mar;80(3):974-997. doi: 10.1177/10519815241289675. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Work. 2025. PMID: 40297886
-
Evidence-Based Strategies for Improving Occupational Safety and Health Among Teleworkers During and After the Coronavirus Pandemic.Hum Factors. 2022 Dec;64(8):1404-1411. doi: 10.1177/0018720820984583. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Hum Factors. 2022. PMID: 33415997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Psychosocial hazards and work-life balance: the role of workplace conflict, rivalry, and harassment in Latvia.Front Psychol. 2025 Feb 20;16:1494288. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1494288. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40051401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathieu E., Ritchie H., Rodés-Guirao L., Appel C., Giattino C., Hasell J., Macdonald B., Saloni D., Beltekian D., Ortiz-Ospina E., et al. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19) [(accessed on 3 June 2024)]. Policy Responses to the Coronavirus Pandemic. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus.
-
- Gartner HR Survey Reveals 41% of Employees Likely to Work Remotely at Least Some of the Time Post Coronavirus Pandemic 2020. [(accessed on 5 May 2024)]. Available online: https://www.gartner.com/en/newsroom/press-releases/2020-04-14-gartner-hr...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources