Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunosuppression in Tiger Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) under Cryptocaryon irritans Infection
- PMID: 39061520
- PMCID: PMC11273842
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14142058
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Immunosuppression in Tiger Pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes) under Cryptocaryon irritans Infection
Abstract
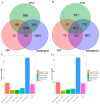
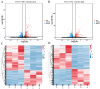
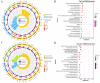
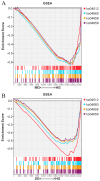
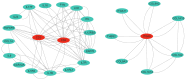
The tiger pufferfish (Takifugu rubripes), also known as fugu, has recently suffered from severe C. irritans infections under aquaculture environment, yet the underlying immune mechanisms against the parasite remain poorly understood. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive transcriptome analysis of the gill tissue from infected and uninfected fish using PacBio long-read (one pooled sample each for seriously infected and healthy individuals, respectively) and Illumina short-read (three pools for mildly infected, seriously infected, and healthy individuals, respectively) RNA sequencing technologies. After aligning sequence data to fugu's reference genome, 47,307 and 34,413 known full-length transcripts were identified and profiled in healthy and infected fish, respectively. Similarly, we identified and profiled 1126 and 803 novel genes that were obtained from healthy and infected fish, respectively. Interestingly, we found a decrease in the number of alternative splicing (AS) events and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) after infection with C. irritans, suggesting that they may be involved in the regulation of the immune response in fugu. There were 687 and 1535 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in moderately and heavily infected fish, respectively, compared to uninfected fish. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses showed that immune-related DEGs in the two comparison groups were mainly enriched in cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions, ECM-receptor interactions, T-cell receptor signaling pathways, Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation, and Th17 cell differentiation pathways. Further analysis revealed that a large number of immune-related genes were downregulated in infected fish relative to uninfected ones, such as CCR7, IL7R, TNFRSF21, CD4, COL2A1, FOXP3B, and ITGA8. Our study suggests that C. irritans is potentially a highly efficient parasite that may disrupt the defense mechanisms of fugu against it. In addition, in combination of short-read RNA sequencing and previous genome-wide association analyses, we identified five key genes (NDUFB6, PRELID1, SMOX, SLC25A4, and DENND1B) that might be closely associated with C. irritans resistance. This study not only provides valuable resources of novel genic transcripts for further research, but also provides new insights into the immune mechanisms underlying C. irritans infection response in farmed fugu.
Keywords: RNA-seq; aquaculture; fugu; immune response; parasite.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Hongxiang Zhang, Haien Zhang, Weidong Li and Yangzhen Li were employed by the company Tangshan Haidu Seafood Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis in Takifugu rubripes and Dicentrarchus labrax gills during Cryptocaryon irritans infection.J Fish Dis. 2021 Mar;44(3):249-262. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13318. Epub 2020 Dec 13. J Fish Dis. 2021. PMID: 33314157
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals immunoregulation mechanism of lncRNA-mRNA in gill and skin of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) in response to Cryptocaryon irritans infection.BMC Genomics. 2022 Mar 15;23(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08431-w. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35287569 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Potential CeRNA Regulatory Mechanism in Takifugu rubripes against Cryptocaryon irritans Infection.Biology (Basel). 2024 Oct 1;13(10):788. doi: 10.3390/biology13100788. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452097 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic variation of locally-infected skin of Epinephelus coioides reveals the mucosal immune mechanism against Cryptocaryon irritans.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017 Jul;66:398-410. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.05.042. Epub 2017 May 17. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28526573
-
Host responses against the fish parasitizing ciliate Cryptocaryon irritans.Parasite Immunol. 2023 Mar;45(3):e12967. doi: 10.1111/pim.12967. Epub 2023 Jan 27. Parasite Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36606416 Review.
References
-
- Cui J.Z., Shen X.Y., Gong Q.L., Yang G.P., Gu Q.Q. Identification of sex markers by cDNA-AFLP in Takifugu rubripes. Aquaculture. 2006;257:30–36. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.03.003. - DOI
-
- Lu Y., Li Y., Bao M.X., Shang F.Q., Wei R.J., Liu F.J., Liu Y., Wang X.L. Comparative transcriptome profiling and functional analysis in the blood of tiger puffer (Takifugu rubripes) in response to acute hypoxia. Aquac. Rep. 2023;30:101618. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2023.101618. - DOI
-
- Tun T., Ogawa K., Wakabayashi H. Pathological changes induced by three myxosporeans in the intestine of cultured tiger puffer, Takifugu rubripes (Temminck and Schlegel) J. Fish Dis. 2002;25:63–72. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2761.2002.00333.x. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

