Updates on Treatment Modalities for Primary Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair
- PMID: 39061630
- PMCID: PMC11276041
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14141493
Updates on Treatment Modalities for Primary Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Repair
Abstract
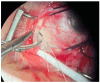
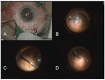
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, a severe eye condition, presents anatomic separation of the neurosensory retina from its outermost layer-the retinal pigment epithelium. Early recognition of this relatively common finding and proper referral of patients to the retinal surgery department is essential in order to minimize its consequent possible severe reduction in vision. Several major surgical methods for the repair of primary rhegmatogenous retinal detachment have been in use over the last several decades, and they all aim to find and close the break in the retina that has caused the detachment. Surgery can be performed as pneumatic retinopexy, pars plana vitrectomy, and/or episcleral surgery (buckling). General surgical trends for reattaching the retina include moving from extraocular to intraocular surgery and from bigger gauge to smaller gauge via minimal invasive vitrectomy surgery (MIVS), with implementing shorter-lasting intraocular tamponades. Surgical options for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment treatment nowadays emphasize gaining retinal reattachment, preferably with one surgery and with minimum damage to the eye. The procedure should not bring secondary eye conditions and complications with severe impairment of visual acuity, and it should be performed on as much as a smaller budget, with possibly peribulbar anesthesia, enabling the patient the quickest possible recovery. It should be adjusted to the patient's condition, not to the surgeon's skills or preferences.
Keywords: equatorial cerclage; pars plana vitrectomy; pneumatic retinopexy; rhegmatogenous retinal detachment; scleral buckling; surgical options.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kohli P., Tripathy K. StatPearls [Internet] StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. Scleral Buckling. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

