Assessment of the Diagnostic Efficacy of Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 39061702
- PMCID: PMC11276230
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14141564
Assessment of the Diagnostic Efficacy of Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: In recent years, there has been an increasing effort to take advantage of the potential use of low magnetic induction devices with less than 1 T, referred to as Low-Field MRI (LF MRI). LF MRI systems were used, especially in the early days of magnetic resonance technology. Over time, magnetic induction values of 1.5 and 3 T have become the standard for clinical devices, mainly because LF MRI systems were suffering from significantly lower quality of the images, e.g., signal-noise ratio. In recent years, due to advances in image processing with artificial intelligence, there has been an increasing effort to take advantage of the potential use of LF MRI with induction of less than 1 T. This overview article focuses on the analysis of the evidence concerning the diagnostic efficacy of modern LF MRI systems and the clinical comparison of LF MRI with 1.5 T systems in imaging the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, and organs of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis.
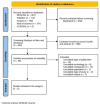
Methodology: A systematic literature review of MEDLINE, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and CENTRAL databases for the period 2018-2023 was performed according to the recommended PRISMA protocol. Data were analysed to identify studies comparing the accuracy, reliability and diagnostic performance of LF MRI technology compared to available 1.5 T MRI.
Results: A total of 1275 publications were retrieved from the selected databases. Only two articles meeting all predefined inclusion criteria were selected for detailed assessment.
Conclusions: A limited number of robust studies on the accuracy and diagnostic performance of LF MRI compared with 1.5 T MRI was available. The current evidence is not sufficient to draw any definitive insights. More scientific research is needed to make informed conclusions regarding the effectiveness of LF MRI technology.
Keywords: diagnostic accuracy; diagnostic efficacy; low field magnetic resonance; magnetic resonance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Sheth K.N., Mazurek M.H., Yuen M.M., Cahn B.A., Shah J.T., Ward A., Kim J.A., Gilmore E.J., Falcone G.J., Petersen N., et al. Assessment of Brain Injury Using Portable, Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Imaging at the Bedside of Critically Ill Patients. JAMA Neurol. 2021;78:41–47. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.3263. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anoardo E., Rodriguez G.G. New challenges and opportunities for low-field MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Open. 2023;14:100086. doi: 10.1016/j.jmro.2022.100086. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources