Validation of Contrast-Enhanced Mammography as Breast Imaging Modality Compared to Standard Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
- PMID: 39061712
- PMCID: PMC11275490
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics14141575
Validation of Contrast-Enhanced Mammography as Breast Imaging Modality Compared to Standard Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
Abstract
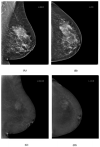
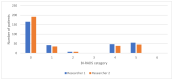
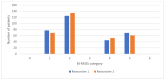
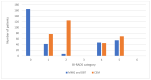
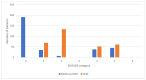
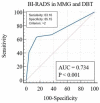
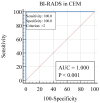
Contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) is a relatively new imaging technique that allows morphologic, anatomic and functional imaging of the breast. The aim of our study was to validate contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) compared to mammography (MMG) and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) in daily clinical practice. This retrospective study included 316 consecutive patients who underwent MMG, DBT and CEM at the Centre for Prevention and Diagnosis of Chronic Diseases of Primorsko-goranska County. Two breast radiologists independently analyzed the image data, without available anamnestic information and without the possibility of comparison with previous images, to determine the presence of suspicious lesions and their morphological features according to the established criteria of the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) lexicon. The diagnostic value of MMG, DBT and CEM was assessed by ROC analysis. The interobserver agreement was excellent. CEM showed higher diagnostic accuracy in terms of sensitivity and specificity compared to MMG and DBT, the reporting time for CEM was significantly shorter, and CEM findings resulted in a significantly lower proportion of equivocal findings (BI-RADS 0), suggesting fewer additional procedures. In conclusion, CEM achieves high diagnostic accuracy while maintaining simplicity, reproducibility and applicability in complex clinical settings.
Keywords: breast cancer; contrast media; digital breast tomosynthesis; mammography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Value of contrast-enhanced mammography combined with the Kaiser score for clinical decision-making regarding tomosynthesis BI-RADS 4A lesions.Eur Radiol. 2022 Nov;32(11):7439-7447. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08810-7. Epub 2022 May 31. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35639141
-
Contrast-Enhanced Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Compared With Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Assessment of Breast Lesions: A Pilot Study.Invest Radiol. 2025 Jun 1;60(6):369-375. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000001138. Epub 2024 Dec 2. Invest Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39621875
-
Multireader comparison of contrast-enhanced mammography versus the combination of digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis in the preoperative assessment of breast cancer.Radiol Med. 2021 Nov;126(11):1407-1414. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01400-5. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Radiol Med. 2021. PMID: 34302599
-
Diagnosis and Staging of Breast Cancer: When and How to Use Mammography, Tomosynthesis, Ultrasound, Contrast-Enhanced Mammography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging.2019 Feb 20. In: Hodler J, Kubik-Huch RA, von Schulthess GK, editors. Diseases of the Chest, Breast, Heart and Vessels 2019-2022: Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2019. Chapter 13. 2019 Feb 20. In: Hodler J, Kubik-Huch RA, von Schulthess GK, editors. Diseases of the Chest, Breast, Heart and Vessels 2019-2022: Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging [Internet]. Cham (CH): Springer; 2019. Chapter 13. PMID: 32096932 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Digital breast tomosynthesis for breast cancer detection: a diagnostic test accuracy systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2020 Apr;30(4):2058-2071. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06549-2. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31900699
References
-
- Sudhir R., Sannapareddy K., Potlapalli A., Krishnamurthy P.B., Buddha S., Koppula V. Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced digital mammography in breast cancer detection in comparison to tomosynthesis, synthetic 2D mammography and tomosynthesis combined with ultrasound in women with dense breast. Br. J. Radiol. 2021;94:1118. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20201046. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mann R.M., Athanasiou A., Baltzer P.A.T., Camps-Herrero J., Clauser P., Fallenberg E.M., Forrai G., Fuchsjäger M.H., Helbich T.H., Killburn-Toppin F., et al. Breast cancer screening in women with extremely dense breasts recommendations of the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI) Eur. Radiol. 2022;32:4036–4045. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08617-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

