Machine Learning and Graph Signal Processing Applied to Healthcare: A Review
- PMID: 39061753
- PMCID: PMC11273494
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11070671
Machine Learning and Graph Signal Processing Applied to Healthcare: A Review
Abstract
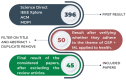
Signal processing is a very useful field of study in the interpretation of signals in many everyday applications. In the case of applications with time-varying signals, one possibility is to consider them as graphs, so graph theory arises, which extends classical methods to the non-Euclidean domain. In addition, machine learning techniques have been widely used in pattern recognition activities in a wide variety of tasks, including health sciences. The objective of this work is to identify and analyze the papers in the literature that address the use of machine learning applied to graph signal processing in health sciences. A search was performed in four databases (Science Direct, IEEE Xplore, ACM, and MDPI), using search strings to identify papers that are in the scope of this review. Finally, 45 papers were included in the analysis, the first being published in 2015, which indicates an emerging area. Among the gaps found, we can mention the need for better clinical interpretability of the results obtained in the papers, that is not to restrict the results or conclusions simply to performance metrics. In addition, a possible research direction is the use of new transforms. It is also important to make new public datasets available that can be used to train the models.
Keywords: deep learning; graph signal processing; health; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Sandryhaila A., Moura J.M. Big data analysis with signal processing on graphs: Representation and processing of massive data sets with irregular structure. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2014;31:80–90. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2014.2329213. - DOI
-
- Chen S., Varma R., Sandryhaila A., Kovačević J. Discrete Signal Processing on Graphs: Sampling Theory. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2015;63:6510–6523. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2469645. - DOI
-
- Giudici P., Sarlin P., Spelta A. The interconnected nature of financial systems: Direct and common exposures. J. Bank. Financ. 2020;112:105149. doi: 10.1016/j.jbankfin.2017.05.010. - DOI
-
- Shi W., Rajkumar R. Point-GNN: Graph neural network for 3d object detection in a point cloud; Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; Seattle, WA, USA. 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1711–1719.
-
- Dong G., Tang M., Wang Z., Gao J., Guo S., Cai L., Gutierrez R., Campbel B., Barnes L.E., Boukhechba M. Graph neural networks in IoT: A survey. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2023;19:1–50. doi: 10.1145/3565973. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 140150/2022-6/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 442238/2023-1/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 312935/2023-4/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 405903/2023-5/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
- 88881.311848/2018-01/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

