Isolation, NMR Characterization, and Bioactivity of a Flavonoid Triglycoside from Anthyllis henoniana Stems: Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Effects on MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 39061863
- PMCID: PMC11273540
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13070793
Isolation, NMR Characterization, and Bioactivity of a Flavonoid Triglycoside from Anthyllis henoniana Stems: Antioxidant and Antiproliferative Effects on MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
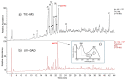
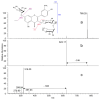
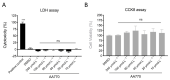
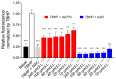
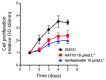
Plant extracts are considered as a large source of active biomolecules, especially in phytosanitary and pharmacological fields. Anthyllis henoniana is a woody Saharan plant located in the big desert of North Africa. Our previous research paper proved the richness of the methanol extract obtained from the stems in flavonoids and phenolic compounds as well as its remarkable antioxidant activity. In this research, we started by investigating the phytochemical composition of the methanol extract using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Among the 41 compounds identified, we isolated and characterized (structurally and functionally) the most abundant product, a flavonoid triglycoside (AA770) not previously described in this species. This compound, which presents no cytotoxic activity, exhibits an interesting cellular antioxidant effect by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and an antiproliferative action on breast cancer cells. This study provides a preliminary investigation into the pharmacological potential of the natural compound AA770, isolated and identified from Anthyllis henoniana for the first time.
Keywords: Anthyllis henoniana; LC–MS/MS; ROS; cell proliferation; cell viability; flavonoids NMR; isorhamnetin-3-O-rutinoside-7-O-rhamnopyranoside; phenolic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ben Younes A., Ben Salem M., El Abed H., Jarraya R. Phytochemical screening and antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic, and antioxidant properties of Anthyllis henoniana (Coss.) flowers extracts in an Alloxan-induced rats model of diabetes. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018;2018:8516302. doi: 10.1155/2018/8516302. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marco J.A., Adell J., Barbera O., Strack D., Wray V. Two isorhamnetin triglycosides from Anthyllis sericea. Phytochemistry. 1989;28:1513–1516. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(00)97777-X. - DOI
-
- Ayachi A., Ben Younes A., Ben Ammar A., Bouzayani B., Samet S., Siala M., Trigui M., Treilhou M., Nathan T., Mezghani-Jarraya R. Effect of the harvest season of Anthyllis henoniana stems on antioxidant and antimicrobial activities: Phytochemical profiling of their ethyl acetate extracts. Molecules. 2023;28:3947. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093947. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ouerfelli M., Majdoub N., Aroussi J., Almajano M.P., Bettaieb Ben Kaâb L. Phytochemical screening and evaluation of the antioxidant and anti-bacterial activity of Woundwort (Anthyllis vulneraria L.) Rev. Bras. Bot. 2021;44:549–559. doi: 10.1007/s40415-021-00736-6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

