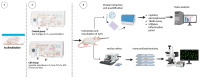
Ocular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress as a Result of Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia: A Rat Model of Sleep Apnea
- PMID: 39061946
- PMCID: PMC11273423
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13070878
Ocular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress as a Result of Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia: A Rat Model of Sleep Apnea
Abstract
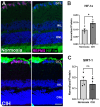
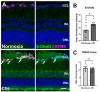
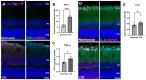
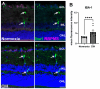
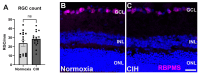
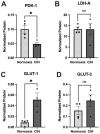
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a sleep disorder characterized by intermittent complete or partial occlusion of the airway. Despite a recognized association between OSA and glaucoma, the nature of the underlying link remains unclear. In this study, we investigated whether mild OSA induces morphological, inflammatory, and metabolic changes in the retina resembling those seen in glaucoma using a rat model of OSA known as chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH). Rats were randomly assigned to either normoxic or CIH groups. The CIH group was exposed to periodic hypoxia during its sleep phase with oxygen reduction from 21% to 10% and reoxygenation in 6 min cycles over 8 h/day. The eyes were subsequently enucleated, and then the retinas were evaluated for retinal ganglion cell number, oxidative stress, inflammatory markers, metabolic changes, and hypoxic response modulation using immunohistochemistry, multiplex assays, and capillary electrophoresis. Statistically significant differences were observed between normoxic and CIH groups for oxidative stress and inflammation, with CIH resulting in increased HIF-1α protein levels, higher oxidative stress marker 8-OHdG, and increased TNF-α. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-1 protein was significantly reduced with CIH. No significant differences were found in retinal ganglion cell number. Our findings suggest that CIH induces oxidative stress, inflammation, and upregulation of HIF-1α in the retina, akin to early-stage glaucoma.
Keywords: chronic intermittent hypoxia; glaucoma; inflammation; obstructive sleep apnea; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sheybani A., Scott R., Samuelson T.W., Kahook M.Y., Bettis D.I., Ahmed I.I.K., Stephens J.D., Kent D., Ferguson T.J., Herndon L.W. Open-Angle Glaucoma: Burden of Illness, Current Therapies, and the Management of Nocturnal IOP Variation. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2020;9:1–14. doi: 10.1007/s40123-019-00222-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

