Advances in Structural and Functional Retinal Imaging and Biomarkers for Early Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy
- PMID: 39061979
- PMCID: PMC11274328
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071405
Advances in Structural and Functional Retinal Imaging and Biomarkers for Early Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
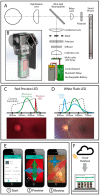
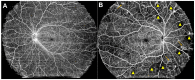
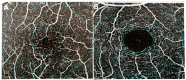
Diabetic retinopathy (DR), a vision-threatening microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus (DM), is a leading cause of blindness worldwide that requires early detection and intervention. However, diagnosing DR early remains challenging due to the subtle nature of initial pathological changes. This review explores developments in multimodal imaging and functional tests for early DR detection. Where conventional color fundus photography is limited in the field of view and resolution, advanced quantitative analysis of retinal vessel traits such as retinal microvascular caliber, tortuosity, and fractal dimension (FD) can provide additional prognostic value. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) has also emerged as a reliable structural imaging tool for assessing retinal and choroidal neurodegenerative changes, which show potential as early DR biomarkers. Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) enables the evaluation of vascular perfusion and the contours of the foveal avascular zone (FAZ), providing valuable insights into early retinal and choroidal vascular changes. Functional tests, including multifocal electroretinography (mfERG), visual evoked potential (VEP), multifocal pupillographic objective perimetry (mfPOP), microperimetry, and contrast sensitivity (CS), offer complementary data on early functional deficits in DR. More importantly, combining structural and functional imaging data may facilitate earlier detection of DR and targeted management strategies based on disease progression. Artificial intelligence (AI) techniques show promise for automated lesion detection, risk stratification, and biomarker discovery from various imaging data. Additionally, hematological parameters, such as neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), may be useful in predicting DR risk and progression. Although current methods can detect early DR, there is still a need for further research and development of reliable, cost-effective methods for large-scale screening and monitoring of individuals with DM.
Keywords: combined measures; deep learning; diabetes mellitus; diagnostic tests; early diabetic retinopathy; optical coherence tomography; optical coherence tomography angiography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Teo Z.L., Tham Y.C., Yu M., Chee M.L., Rim T.H., Cheung N., Bikbov M.M., Wang Y.X., Tang Y., Lu Y., et al. Global Prevalence of Diabetic Retinopathy and Projection of Burden through 2045: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2021;128:1580–1591. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2021.04.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paulus Y.M., Gariano R.F. Diabetic retinopathy: A growing concern in an aging population. Geriatrics. 2009;64:16–20. - PubMed
-
- Tan L., Wang J., Han J., Sainsbury C., Denniston A.K., Crowe F.L., Toulis K.A., Karamat M.A., Yao M., Nirantharakumar K. Socioeconomic Deprivation and the Risk of Sight-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy (STDR): A Population-Based Cohort Study in the U.K. Diabetes Care. 2024;47:844–848. doi: 10.2337/dc23-1626. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
- FFSGIA16002/Fight for Sight
- BJ2023037/Top Talent Support Program for Young and Middle-aged People of Wuxi Health Committee
- 2022043/Elderly Health Research Project of Jiangsu Province
- M202131/Research Project of Wuxi Commission of Health
- BE2022699/Social Development Project of Jiangsu Provincial Department of Science and Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

