Relationship between Serum Sirtuin 1 and Growth Hormone/Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Concentrations in Children with Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature
- PMID: 39062007
- PMCID: PMC11274889
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071433
Relationship between Serum Sirtuin 1 and Growth Hormone/Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 Concentrations in Children with Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature
Abstract
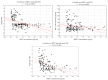
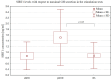
Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) inhibits growth hormone (GH) intracellular signaling for the insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) synthesis via the janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins (STATs) pathway. The aim of this study was to compare SIRT1 concentrations in children with GH deficiency (GHD) and so-called idiopathic short stature (ISS, non-GH deficient), in order to determine the possible impact of changes in serum SIRT1 concentrations on the GH-IGF-1 axis. The study group included 100 short-stature children: 38 with GHD and 62 with ISS (maxGH in two stimulation tests <10 and ≥10 ng/mL, respectively). The control group consisted of 47 healthy, normal-height children. For each child, the concentrations of SIRT1, IGF-1 and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 (IGFBP-3) were determined and the IGF-1/IGFBP-3 molar ratio was calculated. The level of SIRT1 was significantly higher in both groups of short children than in the controls (p < 0.0001), but there were no differences between GHD and ISS (mean ± SD: 0.89 ± 0.45 for ISS; 1.24 ± 0, 86 for GHD; and 0.29 ± 0.21 for controls). A significant negative correlation was found between SIRT1 and height standard deviation score (SDS), IGF-1 and IGF-1/IGFBP-3, but not between SIRT1 and maxGH. Elevated SIRT1 levels may serve as one of the mechanisms through which the secretion of IGF-1 is reduced in children with short stature; however, further research is required to confirm this issue.
Keywords: IGF-1/IGFBP-3 molar ratio; JAK/STATs pathway; growth hormone; growth hormone deficiency; insulin-like growth factor 1; non-GH-deficient children; short stature; sirtuin 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Use of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 (IGFBP-2), IGFBP-3, and IGF-I for assessing growth hormone status in short children.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993 Nov;77(5):1294-9. doi: 10.1210/jcem.77.5.7521346. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1993. PMID: 7521346
-
Plasma levels of insulin-like binding protein-2 in prepubertal short children and its diagnostic value in the evaluation of growth hormone deficiency.Horm Res. 2001;55(3):147-54. doi: 10.1159/000049987. Horm Res. 2001. PMID: 11549877
-
Variable degree of growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor (IGF) sensitivity in children with idiopathic short stature compared with GH-deficient patients: evidence from an IGF-based dosing study of short children.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 May;95(5):2089-98. doi: 10.1210/jc.2009-2139. Epub 2010 Mar 5. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20207829 Clinical Trial.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I deficiency in children with growth hormone insensitivity: current and future treatment options.BioDrugs. 2009;23(3):155-63. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200923030-00002. BioDrugs. 2009. PMID: 19627167 Review.
-
Idiopathic Short Stature and Growth Failure of Unknown Etiology.2023 Oct 24. In: Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Muzumdar R, Purnell J, Rey R, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. 2023 Oct 24. In: Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Muzumdar R, Purnell J, Rey R, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. PMID: 37910635 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Juul A., Dalgaard P., Blum W.F., Bang P., Hall K., Michaelsen K.F., Müller J., Skakkebaek N.E. Serum Levels of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF)-Binding Protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in Healthy Infants, Children, and Adolescents: The Relation to IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-1, IGFBP-2, Age, Sex, Body Mass Index, and Pubertal Maturation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995;80:2534–2542. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.8.7543116. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

