S-Nitroso Human Serum Albumin Enhances Left Ventricle Hemodynamic Performance and Reduces Myocardial Damage after Local Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 39062008
- PMCID: PMC11274172
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071434
S-Nitroso Human Serum Albumin Enhances Left Ventricle Hemodynamic Performance and Reduces Myocardial Damage after Local Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
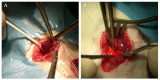
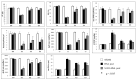
Endothelial nitric oxide (NO) production is crucial in maintaining vascular homeostasis. However, in the context of ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury, uncoupled endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) can exacerbate reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Supplementation with S-nitroso human serum albumin (S-NO-HSA) offers a potential solution by mitigating eNOS uncoupling, thereby enhancing NO bioavailability. In a study conducted at the University of Verona, male rats underwent thoracotomy followed by 30 min left anterior descendant coronary (LAD) occlusion and subsequent reperfusion. Hemodynamic parameters were meticulously assessed using a conductance catheter inserted via the carotid artery. The rats were stratified into two main groups based on reperfusion duration and the timing of drug infusion, with the effects of S-NO-HSA evaluated after 2 or 24 h. Remarkably, intravenous administration of S-NO-HSA, initiated before or during ischemia, exhibited notable benefits. It significantly improved left ventricular function, safeguarded energetic substrates such as phosphocreatine and ATP, and sustained glutathione levels akin to basal conditions, indicative of diminished oxidative stress. The data from this study strongly suggest a protective role for S-NO-HSA in mitigating I/R injury induced by LAD artery occlusion, a phenomenon observed at both 2 and 24 h post-reperfusion. These findings underscore the promising therapeutic potential of NO supplementation in alleviating myocardial damage subsequent to ischemic insult.
Keywords: NO donor; acute myocardial infarction; ischemia–reperfusion damage; nitric oxide; nitrosylated albumin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
S-nitroso human serum albumin reduces ischaemia/reperfusion injury in the pig heart after unprotected warm ischaemia.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 Feb 1;77(3):506-14. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm052. Epub 2007 Oct 30. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18006447
-
S-nitroso human serum albumin treatment reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury in skeletal muscle via nitric oxide release.Circulation. 2002 Jun 25;105(25):3032-8. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000018745.11739.9b. Circulation. 2002. PMID: 12081999
-
The nitric oxide donor, S-nitroso human serum albumin, as an adjunct to HTK-N cardioplegia improves protection during cardioplegic arrest after myocardial infarction in rats.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015 Mar;20(3):387-94. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu383. Epub 2014 Dec 2. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25468794
-
S-nitroso human serum albumin attenuates pulmonary hypertension, improves right ventricular-arterial coupling, and reduces oxidative stress in a chronic right ventricle volume overload model.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015 Mar;34(3):479-88. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2014.09.041. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25511748
-
S-nitroso human serum albumin attenuates ischemia/reperfusion injury after cardioplegic arrest in isolated rabbit hearts.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2005 Dec;24(12):2226-34. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2005.08.004. Epub 2005 Nov 17. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2005. PMID: 16364875
Cited by
-
Associations between the red blood cell distribution width-to-albumin ratio and 3-month outcomes in patients with acute minor ischemic stroke: A cohort study.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 28;20(7):e0329211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329211. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40720528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y., Bissing J.W., Xu L., Ryan A.J., Martin S.M., Miller F.J., Kregel K.C., Buettner G.R., E Kerber R. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors decrease coronary sinus-free radical concentration and ameliorate Myocardial stunning in an ischemia-reperfusion model. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003;38:546–554. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(01)01400-0. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

