The Strong Activation of p53 Tumor Suppressor Drives the Synthesis of the Enigmatic Isoform of DUSP13 Protein
- PMID: 39062022
- PMCID: PMC11274236
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071449
The Strong Activation of p53 Tumor Suppressor Drives the Synthesis of the Enigmatic Isoform of DUSP13 Protein
Abstract
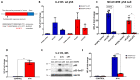
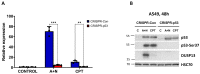
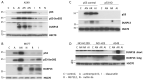
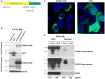
The p53 tumor suppressor protein activates various sets of genes depending on its covalent modifications, which are controlled by the nature and intensity of cellular stress. We observed that actinomycin D and nutlin-3a (A + N) collaborate in inducing activating phosphorylation of p53. Our recent transcriptomic data demonstrated that these substances strongly synergize in the upregulation of DUSP13, a gene with an unusual pattern of expression, coding for obscure phosphatase having two isoforms, one expressed in the testes and the other in skeletal muscles. In cancer cells exposed to A + N, DUSP13 is expressed from an alternative promoter in the intron, resulting in the expression of an isoform named TMDP-L1. Luciferase reporter tests demonstrated that this promoter is activated by both endogenous and ectopically expressed p53. We demonstrated for the first time that mRNA expressed from this promoter actually produces the protein, which can be detected with Western blotting, in all examined cancer cell lines with wild-type p53 exposed to A + N. In some cell lines, it is also induced by clinically relevant camptothecin, by nutlin-3a acting alone, or by a combination of actinomycin D and other antagonists of p53-MDM2 interaction-idasanutlin or RG7112. This isoform, fused with green fluorescent protein, localizes in the perinuclear region of cells.
Keywords: DUSP13; MDM2; alternative promoter; dual-specificity phosphatase; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Łasut-Szyszka B., Małachowska B., Gdowicz-Kłosok A., Krześniak M., Głowala-Kosińska M., Zajkowicz A., Rusin M. Transcriptome Analysis of Cells Exposed to Actinomycin D and Nutlin-3a Reveals New Candidate p53-Target Genes and Indicates That CHIR-98014 Is an Important Inhibitor of p53 Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:11072. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011072. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

