Resistant Starch-Encapsulated Probiotics Attenuate Colorectal Cancer Cachexia and 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Microbial Dysbiosis
- PMID: 39062024
- PMCID: PMC11274618
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071450
Resistant Starch-Encapsulated Probiotics Attenuate Colorectal Cancer Cachexia and 5-Fluorouracil-Induced Microbial Dysbiosis
Abstract
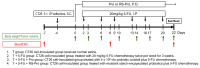
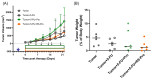
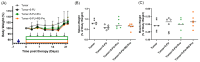
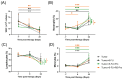
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) is commonly used as the primary chemotherapy for colorectal cancer (CRC). However, it can lead to unwanted chemoresistance. Resistant starch (RS), which functions similarly to fermentable dietary fiber, has the potential to reduce the risk of CRC. The effects of RS on improving CRC-associated cachectic symptoms and 5-FU chemotherapy-induced microbial dysbiosis remain unknown. Female BALB/cByJNarl mice were randomly divided into four groups: one tumor group (with CT26 colonic carcinoma but no treatment) and three CT26 colonic carcinoma-bearing groups that were administered 20 mg/kg 5-FU (T+5-FU group), a probiotic cocktail (4 × 108 CFUs) plus chemotherapy (T+5-FU+Pro), or resistant-starch-encapsulated probiotics plus chemotherapy (T+5-FU+RS-Pro). T+5-FU and T+5-FU+RS-Pro administration significantly suppressed tumor growth and activated apoptotic cell death in CT26-bearing mice. 5-FU-induced increases in inflammatory cytokines and NF-κB signaling were mitigated by the Pro or RS-Pro supplementation. A gut microbial composition comparison indicated that the abundance of intestinal bacteria in the T and T+5-FU groups decreased significantly, while the groups receiving Pro or RS-Pro maintained a greater abundance and healthy gut microbiota composition, suggesting that RS can reduce the microbial dysbiosis that occurs during 5-FU chemotherapy. The use of RS-Pro before chemotherapy should be considered for the regulation of chemotherapy-associated cachectic symptoms, inflammation, and chemotherapy-induced microbial dysbiosis.
Keywords: chemotherapy-enhanced inflammation; colon carcinoma-associated cachectic symptoms; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
C.-H.Y. and M.C.-M.C. were employed by Fecula Biotech Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ministry of Health and Welfare . Health and Vital Statistics in Taiwan. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Executive Yuan; Taipei City, Taiwan: 2023. [(accessed on 31 August 2023)]. Available online: https://dep.mohw.gov.tw/DOS/lp-5069-113-xCat-y112.html.
-
- Ribeiro R.A., Wanderley C.W., Wong D.V., Mota J.M., Leite C.A., Souza M.H., Cunha F.Q., Lima-Júnior R.C. Irinotecan- and 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis: Insights into pathogenesis and therapeutic perspectives. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016;78:881–893. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3139-y. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

