Reducing Oxidative Stress-Mediated Alcoholic Liver Injury by Multiplexed RNAi of Cyp2e1, Cyp4a10, and Cyp4a14
- PMID: 39062078
- PMCID: PMC11274525
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071505
Reducing Oxidative Stress-Mediated Alcoholic Liver Injury by Multiplexed RNAi of Cyp2e1, Cyp4a10, and Cyp4a14
Abstract
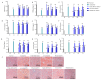
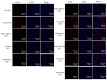
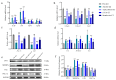
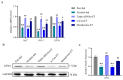
The prevalence of excessive drinking-related alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is rising, yet therapeutic options remain limited. High alcohol consumption and consequent oxidative metabolism by cytochrome P450 (CYP) can lead to extremely high levels of reactive oxygen species, which overwhelm cellular defenses and harm hepatocytes. Our previous investigations showed that inhibiting Cyp2e1 using RNA interference reduced the incidence of ALD. However, compensatory mechanisms other than CYP2E1 contribute to oxidative stress in the liver. Therefore, we coupled triple siRNA lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) targeting Cyp2e1 with two isoenzymes Cyp4a10 and Cyp4a14 to treat ALD mouse models fed with Lieber-Decarli ethanol liquid diet for 12 weeks at the early (1st week), middle (5th week), and late (9th week) stages. The administration of triple siRNA LNPs significantly ameliorated chronic alcoholic liver injury in mice, and early treatment achieved the most profound effects. These effects can be attributed to a reduction in oxidative stress and increased expression of antioxidant genes, including Gsh-Px, Gsh-Rd, and Sod1. Moreover, we observed the alleviation of inflammation, evidenced by the downregulation of Il-1β, Il-6, Tnf-α, and Tgf-β, and the prevention of excessive lipid synthesis, evidenced by the restoration of the expression of Srebp1c, Acc, and Fas. Finally, triple siRNA treatment maintained normal metabolism in lipid oxidation. In brief, our research examined the possible targets for clinical intervention in ALD by examining the therapeutic effects of triple siRNA LNPs targeting Cyp2e1, Cyp4a10, and Cyp4a14. The in vivo knockdown of the three genes in this study is suggested as a promising siRNA therapeutic approach for ALD.
Keywords: alcoholic liver disease; cytochrome P450s; ferroptosis; in vivo RNAi; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Rehm J., Gmel G.E., Sr., Gmel G., Hasan O.S.M., Imtiaz S., Popova S., Probst C., Roerecke M., Room R., Samokhvalov A.V., et al. The relationship between different dimensions of alcohol use and the burden of disease-an update. Addiction. 2017;112:968–1001. doi: 10.1111/add.13757. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2020YFE0205100/The National Key R&D Program of China: Chinese-Australian 'Belt and Road' Joint Laboratory on Traditional Chinese Medicine for the Prevention and Treatment of Severe Infectious Diseases
- 2060302-2004-09/The Central-level Major Increases and Decreases in Expenditure Project
- SH2020036/The Zhenjiang Social Development Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

