Analysis of Ferritin, Hepcidin, Zinc, C-Reactive Protein and IL-6 Levels in COVID-19 in Patients Living at Different Altitudes in Peru
- PMID: 39062181
- PMCID: PMC11275107
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071609
Analysis of Ferritin, Hepcidin, Zinc, C-Reactive Protein and IL-6 Levels in COVID-19 in Patients Living at Different Altitudes in Peru
Abstract
Background: Despite great scientific efforts, understanding the role of COVID-19 clinical biomarkers remains a challenge.
Methods: A cross-sectional descriptive study in two Peruvian cities at different altitudes for comparison: Lima and Huaraz. In each place, three groups were formed, made up of 25 patients with COVID-19 in the ICU, 25 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 who did not require the ICU, and 25 healthy subjects as a control group. Five biomarkers were measured: IL-6, hepcidin, ferritin, C-reactive protein, and zinc using ELISA assays.
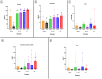
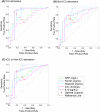
Results: Ferritin, C-reactive protein, and IL-6 levels were significantly higher in the ICU and non-ICU groups at both study sites. In the case of hepcidin, the levels were significantly higher in the ICU group at both study sites compared to the non-ICU group. Among the groups within each study site, the highest altitude area presented statistically significant differences between its groups in all the markers evaluated. In the lower altitude area, differences were only observed between the groups for the zinc biomarker.
Conclusion: COVID-19 patients residing at high altitudes tend to have higher levels of zinc and IL-6 in all groups studied compared to their lower altitude counterparts.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6; ferritin; hepcidin; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard [Internet] World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2022. [(accessed on 26 February 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int.
-
- Wang Y., He Y., Tong J., Qin Y., Xie T., Li J., Li J., Xiang J., Cui Y., Higgs E.S., et al. Characterization of an Asymptomatic Cohort of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infected Individuals Outside of Wuhan, China. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020;71:2132–2138. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa629. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

