The Role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Axis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 39062182
- PMCID: PMC11274428
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12071610
The Role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Axis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
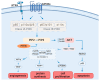
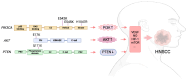
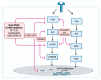
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is one of the most common malignancies globally, representing a significant public health problem with a poor prognosis. The development of efficient therapeutic strategies for HNSCC prevention and treatment is urgently needed. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR (PAM) signaling pathway is a highly conserved transduction network in eukaryotic cells that promotes cell survival, growth, and cycle progression. Dysfunction in components of this pathway, such as hyperactivity of PI3K, loss of PTEN function, and gain-of-function mutations in AKT, are well-known drivers of treatment resistance and disease progression in cancer. In this review, we discuss the major mutations and dysregulations in the PAM signaling pathway in HNSCC. We highlight the results of clinical trials involving inhibitors targeting the PAM signaling pathway as a strategy for treating HNSCC. Additionally, we examine the primary mechanisms of resistance to drugs targeting the PAM pathway and potential therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: HNSCC; PAM signaling pathway; inhibitors; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Ndiaye C., Mena M., Alemany L., Arbyn M., Castellsagué X., Laporte L., Bosch F.X., de Sanjosé S., Trottier H. HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a detection in head and neck cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1319–1331. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70471-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous