Do Moral Emotions Interact with Self-Control and Unstructured Socializing in Explaining Rule-Breaking Behavior Committed Together with Friends?
- PMID: 39062216
- PMCID: PMC11274785
- DOI: 10.3390/children11070766
Do Moral Emotions Interact with Self-Control and Unstructured Socializing in Explaining Rule-Breaking Behavior Committed Together with Friends?
Abstract
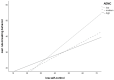
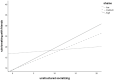
Previous research has shown that moral emotions interact with self-control and unstructured socializing in explaining rule-breaking behavior. High levels of moral emotions appear to weaken the effects of both self-control and unstructured socializing, in explaining rule-breaking behavior. The current study examined whether these interactions also affect rule-breaking behavior that is explicitly committed with friends. In addition, three operationalizations of moral emotions were distinguished. Data were collected from N = 169 adolescents (54% female; mean = 14.95 years; SD = 1.7) using a self-report questionnaire battery. Results indicate that high levels of anticipated emotions in moral conflicts (AEMC) attenuate the effect of low self-control on one's own rule-breaking behavior. In contrast, high levels of both guilt- and shame-proneness enhanced the effect of unstructured socializing on one's own and rule-breaking with friends. The limitations of the study, ideas for future research, and practical implications are also discussed.
Keywords: moral emotions; rule-breaking behavior; self-control; situational action theory; unstructured socializing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Unstructured Socializing with Peers, Low Self-Control, and Substance Use.Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2022 Jan;66(1):3-27. doi: 10.1177/0306624X20967939. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2022. PMID: 33150818
-
The Combined Roles of Moral Emotion and Moral Rules in Explaining Acts of Violence Using a Situational Action Theory Perspective.J Interpers Violence. 2021 Sep;36(17-18):8715-8740. doi: 10.1177/0886260519852634. Epub 2019 Jun 3. J Interpers Violence. 2021. PMID: 31156025
-
[Externalizing problem behavior with friends in adolescence: What role do factors of callous-unemotional traits play?].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2024 Apr;67(4):392-399. doi: 10.1007/s00103-024-03850-4. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2024. PMID: 38478024 Free PMC article. German.
-
Emotion, regulation, and moral development.Annu Rev Psychol. 2000;51:665-97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.51.1.665. Annu Rev Psychol. 2000. PMID: 10751984 Review.
-
A Comparison of the Social-Adaptive Perspective and Functionalist Perspective on Guilt and Shame.Behav Sci (Basel). 2017 Dec 11;7(4):83. doi: 10.3390/bs7040083. Behav Sci (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29232888 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wikström P.H., Treiber K. Situational Theory: The Importance of Interactions and Action Mechanisms in the Explanation of Crime. In: Piquero A.R., editor. The Handbook of Criminological Theory. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2015. pp. 415–444.
-
- Wikström P.-O.H. Situational Action Theory: A General, Dynamic and Mechanism-Based Theory of Crime and Its Causes. In: Krohn M.D., Hendrix N., Lizotte A.J., editors. Handbook on Crime and Deviance. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. 259–281.
-
- Wikström P.-O.H., Svensson R. When Does Self-Control Matter? The Interaction between Morality and Self-Control in Crime Causation. Eur. J. Criminol. 2010;7:395–410. doi: 10.1177/1477370810372132. - DOI
-
- Svensson R., Weerman F.M., Pauwels L.J.R., Bruinsma G.J.N., Bernasco W. Moral Emotions and Offending: Do Feelings of Anticipated Shame and Guilt Mediate the Effect of Socialization on Offending? Eur. J. Criminol. 2013;10:22–39. doi: 10.1177/1477370812454393. - DOI
-
- Dollinger B., Schmidt-Semisch H. Handbuch Jugendkriminalität. Springer; Wiesbaden, Germany: 2018. Sozialpädagogik und Kriminologie im Dialog Einführende Perspektiven zum Ereignis “Jugendkriminalität”.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

