Incidence and Characteristics of Pediatric Patients with Acute Otitis Hospitalized in a Romanian Infectious Diseases Hospital
- PMID: 39062281
- PMCID: PMC11274892
- DOI: 10.3390/children11070832
Incidence and Characteristics of Pediatric Patients with Acute Otitis Hospitalized in a Romanian Infectious Diseases Hospital
Abstract
Background: Otic involvement is common in children during acute infectious diseases, and is an important cause of morbidity and health service utilization.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of pediatric cases hospitalized in the largest infectious disease hospital in Romania between 2018 and 2023, with the aim of quantifying the incidence and impact of acute otitis (AO) according to pediatric age subgroups.
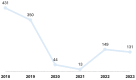
Results: A total of 1118 cases diagnosed with AO were eligible and included in the analysis. Acute congestive otitis media was the most common subtype, identified in 53.3% of cases, followed by acute purulent otitis media (APOM) in 26.7% of children. The majority of AO cases (69.9%) were diagnosed in the pre-pandemic period (2018-2019), and infants (10.6%), toddlers (49.4%), and preschoolers (29.2%) were the most affected age groups. A viral infection associated with the AO episode was documented in 49.6% of cases. Influenza viruses were most commonly reported (20.5%), followed by SARS-CoV-2 (5.8%), and adenovirus (4.9%). A total of 38 cases of AO were identified in children with measles. In 15.9% of APOM cases, Streptococcus pneumoniae was isolated by culture from otic secretions. The duration of hospitalization was longer in children with APOM and acute otitis externa compared to the other subtypes of AO (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Our study highlights the importance of ENT (ear, nose, and throat) monitoring in children hospitalized for acute infectious diseases, as the majority of AO cases occur in the context of a viral infection. These findings emphasize the necessity for tailored assessment and intervention in suspected cases of AO, especially in young children under 5 years of age.
Keywords: acute otitis; children; hospitalization; viral infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ngo C.C., Massa H.M., McMonagle B.A., Perry C.F., Nissen M.D., Sloots T.P., Thornton R.B., Cripps A.W. Predominant Bacterial and Viral Otopathogens Identified Within the Respiratory Tract and Middle Ear of Urban Australian Children Experiencing Otitis Media Are Diversely Distributed. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022;12:775535. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.775535. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Usonis V., Jackowska T., Petraitiene S., Sapala A., Neculau A., Stryjewska I., Devadiga R., Tafalla M., Holl K. Incidence of acute otitis media in children below 6 years of age seen in medical practices in five East European countries. BMC Pediatr. 2016;16:108. doi: 10.1186/s12887-016-0638-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous