Comparison of Metabolic Control in Children and Adolescents Treated with Insulin Pumps
- PMID: 39062288
- PMCID: PMC11275477
- DOI: 10.3390/children11070839
Comparison of Metabolic Control in Children and Adolescents Treated with Insulin Pumps
Abstract
Background: While insulin pumps remain the most common form of therapy for youths with type 1 diabetes (T1DM), they differ in the extent to which they utilize data from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and automate insulin delivery.
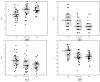
Methods: The aim of the study was to compare metabolic control in patients using different models of insulin pumps. This retrospective single-center study randomly sampled 30 patients for each of the following treatments: Medtronic 720G without PLGS (predictive low glucose suspend), Medtronic 640G or 740G with PLGS and Medtronic 780G. In the whole study group, we used CGM systems to assess patients' metabolic control, and we collected lipid profiles. In three groups of patients, we utilized CGM sensors (Guardian 3, Guardian 4, Libre 2 and Dexcom G6) to measure the following glycemic variability proxy values: time in range (TIR), time below 70 mg/dL (TBR), time above 180 mg/dL (TAR), coefficient of variation (CV) and mean sensor glucose.
Results: Medtronic 640G or 740G and 780G users were more likely to achieve a target time in the target range 70-180 mg/dL (≥80%) [Medtronic 720G = 4 users (13.3%) vs. Medtronic 640G/740G = 10 users (33.3%) vs. Medtronic 780G = 13 users (43.3%); p = 0.0357)] or low glucose variability [Medtronic 720G = 9 users (30%) vs. Medtronic 640G/740G = 18 users (60%) vs. Medtronic 780G = 19 users (63.3%); p = 0.0175)].
Conclusions: Any integration between the insulin pump and CGM was associated with better glycemic control. More advanced technologies and artificial intelligence in diabetes help patients maintain better glycemia by eliminating various factors affecting postprandial glycemia.
Keywords: closed loop; insulin pump; predictive suspend.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Position of the Polish Diabetes Association Current Topics in Diabetes 2024. Curr. Top Diabetes. 2023;3:1–348. doi: 10.5114/ctd/183052. - DOI
-
- Castaneda J., Arrieta A., Heuvel T.V.D., Cohen O. The significance of coefficient of variation as a measure of hypoglycaemia risk and glycaemic control in real world users of the automated insulin delivery MiniMed 780G system. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023;25:2545–2552. doi: 10.1111/dom.15139. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

