Bioengineered Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Anti-Cancer Therapy: Current Trends and Future Prospects
- PMID: 39062449
- PMCID: PMC11275142
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14070734
Bioengineered Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Anti-Cancer Therapy: Current Trends and Future Prospects
Abstract
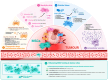
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) are one of the most widely used cell types in advanced therapies due to their therapeutic potential in the regulation of tissue repair and homeostasis, and immune modulation. However, their use in cancer therapy is controversial: they can inhibit cancer cell proliferation, but also potentially promote tumour growth by supporting angiogenesis, modulation of the immune milieu and increasing cancer stem cell invasiveness. This opposite behaviour highlights the need for careful and nuanced use of MSCs in cancer treatment. To optimize their anti-cancer effects, diverse strategies have bioengineered MSCs to enhance their tumour targeting and therapeutic properties or to deliver anti-cancer drugs. In this review, we highlight the advanced uses of MSCs in cancer therapy, particularly as carriers of targeted treatments due to their natural tumour-homing capabilities. We also discuss the potential of MSC-derived extracellular vesicles to improve the efficiency of drug or molecule delivery to cancer cells. Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the therapeutic potential of these cells and setting the stage for future advances in MSC-based cancer treatment. It is critical to identify the broad and potent applications of bioengineered MSCs in solid tumour targeting and anti-cancer agent delivery to position them as effective therapeutics in the evolving field of cancer therapy.
Keywords: anti-cancer therapy; cell therapy; mesenchymal stem/stromal cells; targeted therapy; therapeutic vehicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Therapeutic roles of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Sep 3;14(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01141-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34479611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the tumor microenvironment with mesenchymal stem cells based delivery approach for efficient delivery of anticancer agents: An updated review.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Feb;232:116725. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116725. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39746456 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as novel cell-free therapy for treatment of autoimmune disorders.Exp Mol Pathol. 2021 Feb;118:104566. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104566. Epub 2020 Nov 6. Exp Mol Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33160961 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells as next-generation drug delivery vehicles for cancer therapeutics.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021 Nov;18(11):1627-1642. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2021.1960309. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 34311638 Review.
-
Engineering mesenchymal stem cells: a novel therapeutic approach in breast cancer.J Drug Target. 2020 Aug-Sep;28(7-8):732-741. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2020.1775842. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Drug Target. 2020. PMID: 32463709
Cited by
-
Oncolytic Virus Therapy in a New Era of Immunotherapy, Enhanced by Combination with Existing Anticancer Therapies: Turn up the Heat!J Cancer. 2025 Feb 18;16(6):1782-1793. doi: 10.7150/jca.102285. eCollection 2025. J Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40092697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MSCs regulate oxidative stress through the Nrf2 pathway to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03770-2. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40604620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Puissant B., Barreau C., Bourin P., Clavel C., Corre J., Bousquet C., Taureau C., Cousin B., Abbal M., Laharrague P., et al. Immunomodulatory effect of human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells: Comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2005;129:118–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2005.05409.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

