Biochemical and Functional Profiling of Thioredoxin-Dependent Cytosolic GPX-like Proteins in Euglena gracilis
- PMID: 39062479
- PMCID: PMC11275057
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14070765
Biochemical and Functional Profiling of Thioredoxin-Dependent Cytosolic GPX-like Proteins in Euglena gracilis
Abstract
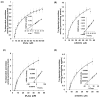
Unlike plants and animals, the phytoflagellate Euglena gracilis lacks catalase and contains a non-selenocysteine glutathione peroxidase-like protein (EgGPXL), two peroxiredoxins (EgPrx1 and EgPrx4), and one ascorbate peroxidase in the cytosol to maintain reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis. In the present study, the full-length cDNA of three cytosolic EgGPXLs was obtained and further characterized biochemically and functionally. These EgGPXLs used thioredoxin instead of glutathione as an electron donor to reduce the levels of H2O2 and t-BOOH. The specific peroxidase activities of these enzymes for H2O2 and t-BOOH were 1.3 to 4.9 and 0.79 to 3.5 µmol/min/mg protein, respectively. Cytosolic EgGPXLs and EgPrx1/EgPrx4 were silenced simultaneously to investigate the synergistic effects of these genes on the physiological function of E. gracilis. The suppression of cytosolic EgGPXL genes was unable to induce any critical phenomena in Euglena under normal (100 μmol photons m-2 s-1) and high-light conditions (350 μmol photons m-2 s-1) at both autotrophic and heterotrophic states. Unexpectedly, the suppression of EgGPXL genes was able to rescue the EgPrx1/EgPrx4-silenced cell line from a critical situation. This study explored the potential resilience of Euglena to ROS, even with restriction of the cytosolic antioxidant system, indicating the involvement of some compensatory mechanisms.
Keywords: Euglena gracilis; cytosolic GPX-like protein; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







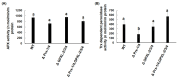



Similar articles
-
Characterization of chloroplastic thioredoxin dependent glutathione peroxidase like protein in Euglena gracilis: biochemical and functional perspectives.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2024 Aug 26;88(9):1034-1046. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbae087. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38925644
-
Identification and functional analysis of peroxiredoxin isoforms in Euglena gracilis.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014;78(4):593-601. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2014.890037. Epub 2014 May 21. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 25036955
-
Euglena gracilis ascorbate peroxidase forms an intramolecular dimeric structure: its unique molecular characterization.Biochem J. 2010 Feb 9;426(2):125-34. doi: 10.1042/BJ20091406. Biochem J. 2010. PMID: 20015051
-
Biochemistry and Physiology of Reactive Oxygen Species in Euglena.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;979:47-64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-54910-1_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28429317 Review.
-
Glutathione peroxidases as redox sensor proteins in plant cells.Plant Sci. 2015 May;234:22-6. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.01.017. Epub 2015 Feb 7. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25804806 Review.
References
-
- Medrano-Macías J., Flores-Gallegos A.C., Nava-Reyna E., Morales I., Tortella G., Solís-Gaona S., Benavides-Mendoza A. Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Species (RONSS) as a Metabolic Cluster for Signaling and Biostimulation of Plants: An Overview. Plants. 2022;23:3203. doi: 10.3390/plants11233203. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Navrot N., Collin V., Gualberto J., Gelhaye E., Hirasawa M., Rey P., Knaff D.B., Issakidis E., Jacquot J.P., Rouhier N. Plant Glutathione Peroxidases are Functional Peroxiredoxins Distributed in Several Subcellular Compartments and Regulated During Biotic and Abiotic Stresses. Plant Physiol. 2006;142:1364–1379. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.089458. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

