Radiation-Induced Endothelial Ferroptosis Accelerates Atherosclerosis via the DDHD2-Mediated Nrf2/GPX4 Pathway
- PMID: 39062593
- PMCID: PMC11274403
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14070879
Radiation-Induced Endothelial Ferroptosis Accelerates Atherosclerosis via the DDHD2-Mediated Nrf2/GPX4 Pathway
Abstract
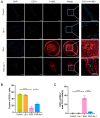
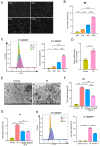
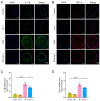
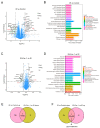
This study sought to explore potential roles of endothelial ferroptosis in radiation-associated atherosclerosis (RAA) and molecular mechanisms behind this phenomenon. Here, an in vivo RAA mouse model was used and treated with ferroptosis inhibitors. We found that the RAA group had a higher plaque burden and a reduction in endothelial cells with increased lipid peroxidation compared to the control group, while ameliorated by liproxstatin-1. In vitro experiments further confirmed that radiation induced the occurrence of ferroptosis in human artery endothelial cells (HAECs). Then, proteomics analysis of HAECs identified domain-containing protein 2 (DDHD2) as a co-differentially expressed protein, which was enriched in the lipid metabolism pathway. In addition, the level of lipid peroxidation was elevated in DDHD2-knockdown HAECs. Mechanistically, a significant decrease in the protein and mRNA expression of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) was observed in HAECs following DDHD2 knockdown. Co-immunoprecipitation assays indicated a potential interaction between DDHD2 and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). The downregulation of Nrf2 protein was also detected in DDHD2-knockdown HAECs. In conclusion, our findings suggest that radiation-induced endothelial ferroptosis accelerates atherosclerosis, and DDHD2 is a potential regulatory protein in radiation-induced endothelial ferroptosis through the Nrf2/GPX4 pathway.
Keywords: DDHD2; Nrf2/GPX4; endothelial injury; ferroptosis; radiation-associated atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tocchetti C.G., Ameri P., de Boer R.A., D’Alessandra Y., Russo M., Sorriento D., Ciccarelli M., Kiss B., Bertrand L., Dawson D., et al. Cardiac dysfunction in cancer patients: Beyond direct cardiomyocyte damage of anticancer drugs: Novel cardio-oncology insights from the joint 2019 meeting of the ESC Working Groups of Myocardial Function and Cellular Biology of the Heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020;116:1820–1834. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa222. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shah B.N., Gujral D.M., Chahal N.S., Harrington K.J., Nutting C.M., Senior R. Plaque Neovascularization Is Increased in Human Carotid Atherosclerosis Related to Prior Neck Radiotherapy: A Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging. 2016;9:668–675. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2015.07.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto Y., Okawa M., Suzuki K., Tateya I., Yoshimura M., Fushimi Y., Kato E.T., Yoshida K., Miyamoto S. Continuous and Early Progression of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness after Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer: 5-Year Prospective Observational Study. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2023;52:543–551. doi: 10.1159/000528622. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

