Combined Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analysis of the Distribution of Flavonoids in the Fibrous Root and Taproot of Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl
- PMID: 39062607
- PMCID: PMC11275391
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15070828
Combined Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analysis of the Distribution of Flavonoids in the Fibrous Root and Taproot of Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl
Abstract
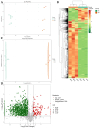
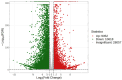
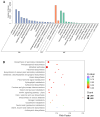
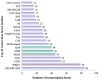
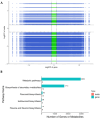
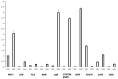
Polygonati rhizoma, known for its distinct yellow rhizomes, is a common therapeutic and culinary plant in Far East Asia. The hue of medicinal plants is closely tied to the flavonoid biosynthesis and content levels. In this research, the fibrous root and taproot of Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl. were studied to explore the secondary metabolite expression and flavonoid biosynthesis mechanisms using transcriptomics and metabolomics. Metabolic analysis identified that the differentially accumulated metabolites (DAMs) in the fibrous root and taproot were predominantly flavonoids, steroids, alkaloids, and phenolic acids. Overall, 200 flavonoids were identified in P. kingianum Coll.et Hemsl., with 170 exhibiting variances between the fibrous root and taproot. The transcriptome analysis revealed that a total of 289 unigenes encoding 32 enzymes were annotated into four flavonoid biosynthesis pathways, which include phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway, flavonoid biosynthesis pathway, isoflavonoid biosynthesis pathway, and flavone and flavonol biosynthesis pathway. The integration of transcriptomic and metabolomic data elucidated that the 76 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) encoding 13 enzyme genes (HCT, CCOMT, C4H, C3'H, CHI, PGT1, FLS, F3'H, CHS, ANR, DFR, F3'5'H, and LAR) and 15 DAMs preferred to be regulated in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway. The expression of 10 DEGs was validated by qRT-PCR, agreeing with the same results by RNA-Seq. These findings shed light into the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites in P. kingianum Coll.et Hemsl., offering valuable information for the sustainable utilization and enhancement of this plant species.
Keywords: Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl.; combined metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis; flavonoid biosynthesis; medicinal plant; roots.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

